Spatiotemporal Expression and Substrate Specificity Analysis of the Cucumber SWEET Gene Family
- PMID: 29163584
- PMCID: PMC5664084
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01855
Spatiotemporal Expression and Substrate Specificity Analysis of the Cucumber SWEET Gene Family
Abstract
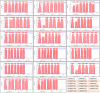
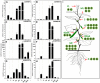
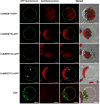
The functions of SWEET (Sugar Will Eventually be Exported Transporter) proteins have been studied in a number of crops, but little is known about their roles in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.), a model plant for studying stachyose metabolism and phloem function. Here, we identified 17 cucumber SWEET genes (CsSWEETs), located on chromosomes 1-6, and classified them into four clades. Two genes from each clade were selected for spatiotemporal expression, subcellular localization, and substrate specificity analyses. Clade I and II proteins were all hexose transporters and targeted to the plasma membrane, while clade III proteins also localized to the plasma membrane, but used sucrose as a substrate. Clade IV SWEET proteins were localized to the tonoplast, and used hexose as a substrate. The eight tested CsSWEET genes were most highly expressed in flower, which represents a large sink in plants. However, each gene also showed specific expression patterns: three of the eight tested genes were highly expressed in mature leaves, two in roots, two in fruit, two in stems, and one was detected in all tested organs. The likely biological roles of each are discussed based on the above results.
Keywords: SWEET transporters; cucumber; phylogeny; spatiotemporal expression; subcellular localization; substrate specificity; sugar.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Functional characterization and expression analysis of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) hexose transporters, involving carbohydrate partitioning and phloem unloading in sink tissues.Plant Sci. 2015 Aug;237:46-56. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.05.006. Epub 2015 May 18. Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 26089151
-
Functional Characterization of CsSWEET5a, a Cucumber Hexose Transporter That Mediates the Hexose Supply for Pollen Development and Rescues Male Fertility in Arabidopsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):1332. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021332. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279332 Free PMC article.
-
SWEET Transporters and the Potential Functions of These Sequences in Tea (Camellia sinensis).Front Genet. 2021 Mar 31;12:655843. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.655843. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33868386 Free PMC article.
-
Co-option of developmentally regulated plant SWEET transporters for pathogen nutrition and abiotic stress tolerance.IUBMB Life. 2015 Jul;67(7):461-71. doi: 10.1002/iub.1394. Epub 2015 Jul 15. IUBMB Life. 2015. PMID: 26179993 Review.
-
Sugar Transporters in Plants: New Insights and Discoveries.Plant Cell Physiol. 2017 Sep 1;58(9):1442-1460. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx090. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28922744 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of SWEET gene family in Litchi chinensis reveal the involvement of LcSWEET2a/3b in early seed development.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Nov 14;19(1):499. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2120-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31726992 Free PMC article.
-
Enzyme Repertoires and Genomic Insights into Lycium barbarum Pectin Polysaccharide Biosynthesis.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2025 Jan 15;22(6):qzae079. doi: 10.1093/gpbjnl/qzae079. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2025. PMID: 39495135 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the SWEET gene family and functional characterization of PsSWEET1a and PsSWEET17b in the regulation of sugar accumulation in 'Fengtang' plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.).BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Apr 1;25(1):407. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06407-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40165087 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor-like kinase SlRLK-like positively regulates sugar accumulation and fruit ripening in tomato.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Aug 20;16:1649082. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1649082. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40909904 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of CLE gene family and their potential roles in bolting and fruit bearing in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Mar 19;21(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02900-2. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33740893 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

