Response to inhaled loxapine in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder: PANSS-EC responder analyses
- PMID: 29163985
- PMCID: PMC5680528
- DOI: 10.1192/bjpo.bp.117.005363
Response to inhaled loxapine in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder: PANSS-EC responder analyses
Abstract
Background: Efficacy of inhaled loxapine 5 or 10 mg in treating agitation was shown using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale - Excited Component (PANSS-EC) in two Phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in 344 agitated patients with schizophrenia and 314 patients with bipolar I disorder (Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT00628589, NCT00721955).
Aims: To examine the five individual items comprising the PANSS-EC and the percentage of patients achieving a clinical response (reduction of ≥40%) in PANSS-EC (Response-40) for these two studies.
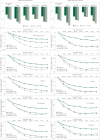
Method: Response-40 was examined at the primary end-point (2 h) and over time.
Results: Response-40 and each PANSS-EC item score were statistically significant v. placebo at 2 h and at each assessment time point for both doses.
Conclusions: Inhaled loxapine produced rapid improvement in agitated patients with schizophrenia or bipolar I disorder, achieving Response-40 at the first assessment (10 min post dose). These results highlight the effectiveness of loxapine across all components of agitation as measured by the PANSS-EC.
Declaration of interest: S.Z. is a member of the speakers bureau for Grupo Ferrer. L.Z. has been a speaker and grant recipient for Teva Pharmaceuticals. J.V.C. and D.A.S. were employees of Alexza Pharmaceuticals during execution of the studies, and are currently paid consultants for and have received stock and/or stock options from Alexza Pharmaceuticals. P.P.Y. is a full-time employee and receives stock options from Teva Pharmaceuticals.
Copyright and usage: © The Royal College of Psychiatrists 2017. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Non-Commercial, No Derivatives (CC BY-NC-ND) license.
Figures
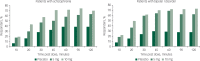

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5). APA, 2013.
-
- Alderfer BS, Allen MH. Treatment of agitation in bipolar disorder across the life cycle. J Clin Psychiatry 2003; 64 (suppl 4): 3–9. - PubMed
-
- Hankin CS, Bronstone A, Koran LM. Agitation in the inpatient psychiatric setting: a review of clinical presentation, burden, and treatment. J Psychiatr Pract 2011; 17: 170–85. - PubMed
-
- Marder SR. A review of agitation in mental illness: treatment guidelines and current therapies. J Clin Psychiatry 2006; 67 (suppl 10): 13–21. - PubMed
-
- Nordstrom K, Allen MH. Alternative delivery systems for agents to treat acute agitation: progress to date. Drugs 2013; 73: 1783–92. - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

