The endocannabinoid system in pain and inflammation: Its relevance to rheumatic disease
- PMID: 29164003
- PMCID: PMC5685274
- DOI: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2017.17025
The endocannabinoid system in pain and inflammation: Its relevance to rheumatic disease
Abstract
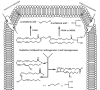
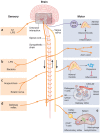
Pain is the most common manifestation of both acute and chronic inflammation that often challenges patients with rheumatic disease. Simply, we attribute this to local joint changes of pH in joints, the formation of radicals, enhanced joint pressure, or cytokine release acting on local nerves to produce pain. However, there is a more complex interplay of interactions between cytokines, mediators of inflammation, and ion channels that influence the final immune response and our perception of pain. Endocannabinoids, a group of less well-known endogenous bioactive lipids, have such manifold immunomodulatory effects able to influence both inflammation and pain. In this review, we overview the endocannabinoid system, its role in pain, inflammation, and immune regulation, and highlight the emerging challenges and therapeutic hopes.
Keywords: Endocannabinoids; arthritis; inflammation; pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Mechoulam R, Devane WA, Breuer A, Zahalka J. A random walk through a cannabis field. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1991;40:461–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(91)90347-75. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Russo EB. History of cannabis and its preparations in saga, science, and sobriquet. Chem Biodivers. 2007;4:1614–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbdv.200790144. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hohmann AG. Spinal and peripheral mechanisms of cannabinoid antinociception: behavioural, neurophysiological and neuroanatomical perspectives. Chem Phys Lipids. 2002;121:173–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-3084(02)00154-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Walker JM, Huang SM. Endocannabinoids in pain modulation. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2002;66:235–42. https://doi.org/10.1054/plef.2001.0361. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Richardson JD, Aanonsen L, Hargreaves KM. Antihyperalgesic effects of spinal cannabinoids. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;345:145–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(97)01621-X. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
