microRNAs and Acute Myeloid Leukemia Chemoresistance: A Mechanistic Overview
- PMID: 29164055
- PMCID: PMC5674931
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2017.00255
microRNAs and Acute Myeloid Leukemia Chemoresistance: A Mechanistic Overview
Abstract
Up until the early 2000s, a functional role for microRNAs (miRNAs) was yet to be elucidated. With the advent of increasingly high-throughput and precise RNA-sequencing techniques within the last two decades, it has become well established that miRNAs can regulate almost all cellular processes through their ability to post-transcriptionally regulate a majority of protein-coding genes and countless other non-coding genes. In cancer, miRNAs have been demonstrated to play critical roles by modifying or controlling all major hallmarks including cell division, self-renewal, invasion, and DNA damage among others. Before the introduction of anthracyclines and cytarabine in the 1960s, acute myeloid leukemia (AML) was considered a fatal disease. In decades since, prognosis has improved substantially; however, long-term survival with AML remains poor. Resistance to chemotherapy, whether it is present at diagnosis or induced during treatment is a major therapeutic challenge in the treatment of this disease. Certain mechanisms such as DNA damage response and drug targeting, cell cycling, cell death, and drug trafficking pathways have been shown to be further dysregulated in treatment resistant cancers. miRNAs playing key roles in the emergence of these drug resistance phenotypes have recently emerged and replacement or inhibition of these miRNAs may be a viable treatment option. Herein, we describe the roles miRNAs can play in drug resistant AML and we describe miRNA-transcript interactions found within other cancer states which may be present within drug resistant AML. We describe the mechanisms of action of these miRNAs and how they can contribute to a poor overall survival and outcome as well. With the precision of miRNA mimic- or antagomir-based therapies, miRNAs provide an avenue for exquisite targeting in the therapy of drug resistant cancers.
Keywords: RNA therapy; acute myeloid leukemia; chemotherapy; cytarabine; daunorubicin; drug resistance; microRNA.
Figures
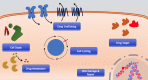
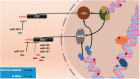

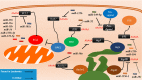
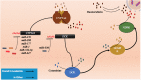

References
-
- Crespo-Solis E, Contreras-Cisneros J, Demichelis-Gómez R, Rosas-López A, Vera-Zertuche JM, Aguayo A, et al. Survival and treatment response in adults with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with a modified international consortium on acute promyelocytic leukemia protocol. Rev Bras Hematol Hemoter (2016) 38(4):285–90. 10.1016/j.bjhh.2016.08.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

