The Prevalence of Overfat Adults and Children in the US
- PMID: 29164096
- PMCID: PMC5671970
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2017.00290
The Prevalence of Overfat Adults and Children in the US
Abstract
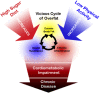
The overfat condition is defined as excess body fat sufficient to impair health. The problem exists in most overweight and obese individuals and can also occur in those who are normal-weight and non-obese, often due to excess abdominal fat. Despite previous indications that the prevalence overweight and obesity is leveling, these conditions are currently at their highest levels in US history. Our review estimated the number of overfat Americans at 91% for adults and 69% for children. The primary purpose of this review was to build upon previous estimations of overfat prevalence in developed countries by using new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to estimate the overfat prevalence in American adults (≥20 years) and children (2-19 years), and to expand the definition of overfat as excess body fat associated with at least one additional risk factor of impaired cardiometabolic or physical health. The secondary goals are to highlight the role of dietary sugar as a primary cause of the overfat pandemic and mention new data showing the increased prevalence of exercise that parallels the rising prevalence of overfat to further emphasize the secondary role exercise may play in fat loss. Current public health guidelines to address the overfat pandemic may require more emphasis on reducing the consumption of refined carbohydrates, including added sugars.
Keywords: chronic disease; inflammation; insulin resistance; obesity; overfat; overweight.
Figures
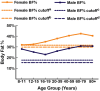
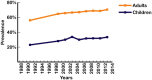
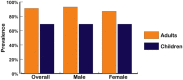

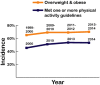
Similar articles
-
Overfat Adults and Children in Developed Countries: The Public Health Importance of Identifying Excess Body Fat.Front Public Health. 2017 Jul 24;5:190. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2017.00190. eCollection 2017. Front Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28791284 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the Global Overfat Pandemic.Front Public Health. 2020 Feb 25;8:51. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00051. eCollection 2020. Front Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32158742 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of web-based programs on the reduction of childhood obesity in school-aged children: A systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-14. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-248. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820152
-
Exercise in weight management of obesity.Cardiol Clin. 2001 Aug;19(3):459-70. doi: 10.1016/s0733-8651(05)70229-0. Cardiol Clin. 2001. PMID: 11570117 Review.
-
The role of resistance training for treatment of obesity related health issues and for changing health status of the individual who is overfat or obese: a review.J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2015 Mar;55(3):205-22. Epub 2014 Oct 10. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2015. PMID: 25303063 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the income-related inequality in obesity among the elderly in China: A decomposition analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 9;10:918630. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.918630. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36159301 Free PMC article.
-
Rethinking COVID-19 and Beyond: Prevention, Remedies, and Recovery.Front Public Health. 2022 Feb 23;10:748498. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.748498. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35284402 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric cancer after gastric bypass with fundectomy: The possibility for early diagnosis.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019;55:156-159. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.01.040. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30739871 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Two intersecting pandemics.Eur J Clin Invest. 2020 Oct;50(10):e13338. doi: 10.1111/eci.13338. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Eur J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32589264 Free PMC article. Review.
-
General and abdominal obesity prevelances and their relations with metabolic syndrome components.Pak J Med Sci. 2019 Jul-Aug;35(4):945-950. doi: 10.12669/pjms.35.4.235. Pak J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31372122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, Thomson B, Graetz N, Margono C, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet (2014) 384(9945):766–81.10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Disability and Risk Factors: Obesity and Overweight. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; (2017). Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/obesity-overweight.htm
-
- National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). Health, United States: With Special Feature on Racial and Ethnic Disparities. Hyattsville, MD: Centers for Disease Control; (2016). Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/hus15.pdf - 053 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

