The Rosiglitazone-Like Effects of Vitexilactone, a Constituent from Vitex trifolia L. in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes
- PMID: 29165364
- PMCID: PMC6150318
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22112030
The Rosiglitazone-Like Effects of Vitexilactone, a Constituent from Vitex trifolia L. in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes
Abstract
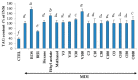
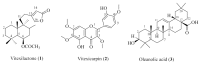
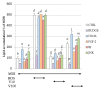
The increased number of patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) has become a worldwide problem, and insulin sensitizers such as thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are used as therapeutic agents. We found that extracts of Vitex trifolia L. (V. trifolia), a medicinal plant from Myanmar, induced adipogenesis similar to rosiglitazone (ROS), which is a TZD, in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. In the present study, we attempted to isolate from V. trifolia those compounds that showed ROS-like effects. Among the extracts of hexane, ethyl acetate, and methanol obtained from V. trifolia, the ethyl acetate extract with the strongest ROS-like effects was purified by various chromatographic methods to obtain three known compounds: vitexilactone (1), vitexicarpin (2) and oleanolic acid (3). Among the isolated compounds, the ROS-like action of 1 was the strongest. The effects of 1 on 3T3-L1 cells during adipogenesis were compared with those of ROS. Both 1 and ROS increased lipid accumulation, the expression of adiponectin and GLUT4 in the cell membrane and decreased both the size of adipocytes and the phosphorylation of IRS-1, ERK1/2 and JNK in 3T3-L1 cells. In contrast, unlike ROS, the induction of proteins involved in lipogenesis was partial. ROS-like effects of 1 in 3T3-L1 cells were suppressed by the addition of bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE), one of a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) antagonists, suggesting that the action of 1 on adipocytes is mediated by PPARγ. From the results of the present study, it can be concluded that 1 is a novel insulin sensitizer candidate.
Keywords: Vitex trifolia L.; adipogenesis; lipogenesis; lipolysis; rosiglitazone; vitexilactone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
(-)-O-Methylcubebin from Vitex trifolia Enhanced Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Cells via the Inhibition of ERK1/2 and p38MAPK Phosphorylation.Molecules. 2019 Dec 24;25(1):73. doi: 10.3390/molecules25010073. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31878261 Free PMC article.
-
Chebulagic acid from Terminalia chebula enhances insulin mediated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via PPARγ signaling pathway.Biofactors. 2014 Nov-Dec;40(6):646-57. doi: 10.1002/biof.1193. Epub 2014 Dec 20. Biofactors. 2014. PMID: 25529897
-
Trichostatin A modulates thiazolidinedione-mediated suppression of tumor necrosis factor α-induced lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 9;8(8):e71517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0071517. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951179 Free PMC article.
-
Search for new type of PPARγ agonist-like anti-diabetic compounds from medicinal plants.Biol Pharm Bull. 2014;37(6):884-91. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b14-00037. Biol Pharm Bull. 2014. PMID: 24882400 Review.
-
Cellular models for the evaluation of the antiobesity effect of selected phytochemicals from food and herbs.J Food Drug Anal. 2017 Jan;25(1):100-110. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2016.10.018. Epub 2016 Dec 7. J Food Drug Anal. 2017. PMID: 28911527 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
(-)-O-Methylcubebin from Vitex trifolia Enhanced Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Cells via the Inhibition of ERK1/2 and p38MAPK Phosphorylation.Molecules. 2019 Dec 24;25(1):73. doi: 10.3390/molecules25010073. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31878261 Free PMC article.
-
CYP76BK1 orthologs catalyze furan and lactone ring formation in clerodane diterpenoids across the mint family.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 29:2024.08.28.609960. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.28.609960. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Plant J. 2024 Nov;120(3):984-997. doi: 10.1111/tpj.17031. PMID: 39257772 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Five genes influenced by obesity may contribute to the development of thyroid cancer through the regulation of insulin levels.PeerJ. 2020 Jul 28;8:e9302. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9302. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33240576 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Vitex trifolia L. leaf extracts and phytoconstituents on cytokine production in human U937 macrophages.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020 Mar 18;20(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-02884-w. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32188443 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive review of ethnomedicinal approaches, phytochemical analysis, and pharmacological potential of Vitex trifolia L.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Mar 21;15:1322083. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1322083. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38576489 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Xu H., Barnes G.T., Yang Q., Tan G., Yang D., Chou C.J., Sole J., Nichols A., Ross J.S., Tartaglia L.A., et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003;112:1821–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI200319451. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lo Furno D., Graziano A.C., Avola R., Giuffrida R., Perciavalle V., Bonina F., Mannino G., Cardile V. A Citrus Bergamia Extract Decreases Adipogenesis and Increases Lipolysis by Modulating PPAR Levels in Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Adipose Tissue. PPAR Res. 2016;2016:4563815. doi: 10.1155/2016/4563815. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

