The Rosiglitazone-Like Effects of Vitexilactone, a Constituent from Vitex trifolia L. in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes
- PMID: 29165364
- PMCID: PMC6150318
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22112030
The Rosiglitazone-Like Effects of Vitexilactone, a Constituent from Vitex trifolia L. in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes
Abstract
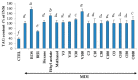
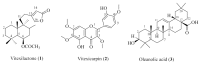
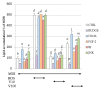
The increased number of patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) has become a worldwide problem, and insulin sensitizers such as thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are used as therapeutic agents. We found that extracts of Vitex trifolia L. (V. trifolia), a medicinal plant from Myanmar, induced adipogenesis similar to rosiglitazone (ROS), which is a TZD, in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. In the present study, we attempted to isolate from V. trifolia those compounds that showed ROS-like effects. Among the extracts of hexane, ethyl acetate, and methanol obtained from V. trifolia, the ethyl acetate extract with the strongest ROS-like effects was purified by various chromatographic methods to obtain three known compounds: vitexilactone (1), vitexicarpin (2) and oleanolic acid (3). Among the isolated compounds, the ROS-like action of 1 was the strongest. The effects of 1 on 3T3-L1 cells during adipogenesis were compared with those of ROS. Both 1 and ROS increased lipid accumulation, the expression of adiponectin and GLUT4 in the cell membrane and decreased both the size of adipocytes and the phosphorylation of IRS-1, ERK1/2 and JNK in 3T3-L1 cells. In contrast, unlike ROS, the induction of proteins involved in lipogenesis was partial. ROS-like effects of 1 in 3T3-L1 cells were suppressed by the addition of bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE), one of a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) antagonists, suggesting that the action of 1 on adipocytes is mediated by PPARγ. From the results of the present study, it can be concluded that 1 is a novel insulin sensitizer candidate.
Keywords: Vitex trifolia L.; adipogenesis; lipogenesis; lipolysis; rosiglitazone; vitexilactone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Xu H., Barnes G.T., Yang Q., Tan G., Yang D., Chou C.J., Sole J., Nichols A., Ross J.S., Tartaglia L.A., et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003;112:1821–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI200319451. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lo Furno D., Graziano A.C., Avola R., Giuffrida R., Perciavalle V., Bonina F., Mannino G., Cardile V. A Citrus Bergamia Extract Decreases Adipogenesis and Increases Lipolysis by Modulating PPAR Levels in Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Adipose Tissue. PPAR Res. 2016;2016:4563815. doi: 10.1155/2016/4563815. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

