Interventions for managing skeletal muscle spasticity following traumatic brain injury
- PMID: 29165784
- PMCID: PMC6486165
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008929.pub2
Interventions for managing skeletal muscle spasticity following traumatic brain injury
Abstract
Background: Skeletal muscle spasticity is a major physical complication resulting from traumatic brain injury (TBI), which can lead to muscle contracture, joint stiffness, reduced range of movement, broken skin and pain. Treatments for spasticity include a range of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions, often used in combination. Management of spasticity following TBI varies from other clinical populations because of the added complexity of behavioural and cognitive issues associated with TBI.
Objectives: To assess the effects of interventions for managing skeletal muscle spasticity in people with TBI.
Search methods: In June 2017, we searched key databases including the Cochrane Injuries Group Specialised Register, CENTRAL, MEDLINE (Ovid), Embase (Ovid) and others, in addition to clinical trials registries and the reference lists of included studies.
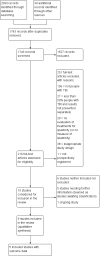
Selection criteria: We included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and cross-over RCTs evaluating any intervention for the management of spasticity in TBI. Only studies where at least 50% of participants had a TBI (or for whom separate data for participants with TBI were available) were included. The primary outcomes were spasticity and adverse effects. Secondary outcome measures were classified according to the World Health Organization International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health including body functions (sensory, pain, neuromusculoskeletal and movement-related functions) and activities and participation (general tasks and demands; mobility; self-care; domestic life; major life areas; community, social and civic life).
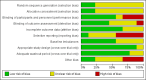
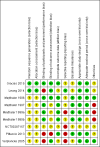
Data collection and analysis: We used standard methodological procedures expected by Cochrane. Data were synthesised narratively; meta-analysis was precluded due to the paucity and heterogeneity of data.
Main results: We included nine studies in this review which involved 134 participants with TBI. Only five studies reported between-group differences, yielding outcome data for 105 participants with TBI. These five studies assessed the effects of a range of pharmacological (baclofen, botulinum toxin A) and non-pharmacological (casting, physiotherapy, splints, tilt table standing and electrical stimulation) interventions, often in combination. The studies which tested the effect of baclofen and tizanidine did not report their results adequately. Where outcome data were available, spasticity and adverse events were reported, in addition to some secondary outcome measures.Of the five studies with results, three were funded by governments, charities or health services and two were funded by a pharmaceutical or medical technology company. The four studies without useable results were funded by pharmaceutical or medical technology companies.It was difficult to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of these interventions due to poor reporting, small study size and the fact that participants with TBI were usually only a proportion of the overall total. Meta-analysis was not feasible due to the paucity of data and heterogeneity of interventions and comparator groups. Some studies concluded that the intervention they tested had beneficial effects on spasticity, and others found no difference between certain treatments. The most common adverse event was minor skin damage in people who received casting. We believe it would be misleading to provide any further description of study results given the quality of the evidence was very low for all outcomes.
Authors' conclusions: The very low quality and limited amount of evidence about the management of spasticity in people with TBI means that we are uncertain about the effectiveness or harms of these interventions. Well-designed and adequately powered studies using functional outcome measures to test the interventions used in clinical practice are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Kate Phillips is the director of a private multidisciplinary community rehabilitation service and is a practising neurological physiotherapist, treating people who have had a TBI. Kate is a clinical consultant on the Clinical Panel of the Transport Accident Commission in Victoria, Australia. The Transport Accident Commission is a Victorian Government owned organisation, its role is to pay for treatment and benefits for people injured in transport accidents.
All authors were supported to complete this work by a grant received from the Transport Accident Commission, Victoria.
AS, MC, VP, DO, RG, JW, OC and LP declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
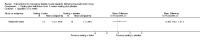



Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008929
References
References to studies included in this review
Gracies 2015 {published data only}
-
- Gracies JM, Brashear A, Jech R, McAllister P, Banach M, Valkovic P, et al. Safety and efficacy of abobotulinumtoxinA for hemiparesis in adults with upper limb spasticity after stroke or traumatic brain injury: a double‐blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet Neurology 2015;14:992‐1001. - PubMed
-
- O'Dell MW, Walker HW, Edgley SR, Gracies JM, Gul F, Wimmer M, et al. AbobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®) in the treatment of adult patients with upper limb spasticity due to traumatic brain injury. PM & R : the Journal of Injury, Function, and Rehabilitation 2015;7:S103.
Leung 2014 {published data only}
-
- Leung J, Harvey LA, Moseley AM, Whiteside B, Simpson M, Stroud K. Standing with electrical stimulation and splinting is no better than standing alone for management of ankle plantarflexion contractures in people with traumatic brain injury: a randomised trial. Journal of Physiotherapy 2014;60:201‐8. - PubMed
Meythaler 1996 {published data only}
-
- Meythaler JM, DeVivo MJ, Hadley M. Prospective study on the use of bolus intrathecal baclofen for spastic hypertonia due to acquired brain injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1996; Vol. 77, issue 5:461‐6. - PubMed
Meythaler 1997 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Meythaler JM, McCary A, Hadley MN. Prospective assessment of continuous intrathecal infusion of baclofen for spasticity caused by acquired brain injury: a preliminary report. Journal of Neurosurgery 1997; Vol. 87, issue 3:415‐9. - PubMed
Meythaler 1999a {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Meythaler JM, Guin‐Renfroe S, Hadley MN. Continuously infused intrathecal baclofen for spastic/dystonic hemiplegia: a preliminary report. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 1999; Vol. 78, issue 3:247‐54. - PubMed
Meythaler 1999b {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Meythaler JM, Guin‐Renfroe S, Grabb P, Hadley MN. Long‐term continuously infused intrathecal baclofen for spastic‐dystonic hypertonia in traumatic brain injury: 1‐year experience. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1999; Vol. 80, issue 1:13‐9. - PubMed
NCT00287157 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- NCT00287157. Pilot, proof‐of‐concept study of sublingual tizanidine in children with chronic traumatic brain injury (TBI). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00287157 Date first received: 6 February 2006.
Pittaccio 2013 {published data only}
-
- Pittaccio S, Garavaglia L, Viscuso S, Beretta E, Strazzer S. Implementation, testing and pilot clinical evaluation of superelastic splints that decrease joint stiffness. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 2013;41:2003‐17. - PubMed
Verplancke 2005 {published data only}
-
- Verplancke D, Snape S, Salisbury CF, Jones PW, Ward AB. A randomized controlled trial of botulinum toxin on lower limb spasticity following acute acquired severe brain injury. Clinical Rehabilitation 2005; Vol. 19, issue 2:117‐25. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Armstrong 1997 {published data only}
-
- Armstrong RW, Steinbok P, Cochrane DD, Kube SD, Fife SE, Farrell K. Intrathecally administered baclofen for treatment of children with spasticity of cerebral origin. Journal of Neurosurgery 1997;87(3):409‐14. - PubMed
Ashby 1972 {published data only}
Baricich 2008 {published data only}
-
- Baricich A, Carda S, Bertoni M, Maderna L, Cisari C. A single‐blinded, randomized pilot study of botulinum toxin type a combined with non‐pharmacological treatment for spastic foot. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2008; Vol. 40, issue 10:870‐2. - PubMed
Barnes 2010 {published data only}
-
- Barnes M, Schnitzler A, Medeiros L, Aguilar M, Lehnert‐Batar A, Minnasch P. Efficacy and safety of NT 201 for upper limb spasticity of various etiologies ‐ a randomized parallel‐group study. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica 2010; Vol. 122, issue 4:295‐302. - PubMed
Basmajian 1973 {published data only}
-
- Basmajian JV, Super GA. Dantrolene sodium in the treatment of spasticity. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1973; Vol. 54, issue 2:61‐4. - PubMed
Basmajian 1974 {published data only}
-
- Basmajian JV, Yucel V. Effects of a GABA‐derivative (BA‐34647) on spasticity. Preliminary report of a double‐blind cross‐over study. American Journal of Physical Medicine 1974; Vol. 53, issue 5:223‐8. - PubMed
Bensmail 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bensmail D, Robertson JVG, Fermanian C, Roby‐Brami A. Botulinum toxin to treat upper‐limb spasticity in hemiparetic patients: analysis of function and kinematics of reaching movements. Neurorehabilitation & Neural Repair 2010; Vol. 24, issue 3:273‐81. - PubMed
Bes 1988 {published data only}
-
- Bes A, Eyssette M, Pierrot‐Deseilligny E, Rohmer F, Warter JM. A multi‐centre, double‐blind trial of tizanidine, a new antispastic agent, in spasticity associated with hemiplegia. Current Medical Research and Opinion 1988; Vol. 10, issue 10:709‐18. - PubMed
Bovend'Eerdt 2009 {published data only}
-
- Bovend'Eerdt TJH, Dawes H, Sackley C, Izadi H, Wade DT. Mental techniques during manual stretching in spasticity ‐ a pilot randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2009; Vol. 23, issue 2:137‐45. [0269‐2155] - PubMed
Boyd 2001 {published data only}
-
- Boyd RN, Dobson F, Parrott J, Love S, Oates J, Larson A, et al. The effect of botulinum toxin type A and a variable hip abduction orthosis on gross motor function: a randomized controlled trial. European Journal of Neurology 2001; Vol. 8, issue Suppl 5:109‐19. - PubMed
Burbaud 1996 {published data only}
-
- Burbaud P, Wiart L, Dubos JL, Gaujard E, Debelleix X, Joseph PA, et al. A randomised, double blind, placebo controlled trial of botulinum toxin in the treatment of spastic foot in hemiparetic patients. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry. 1996/09/01 1996; Vol. 61, issue 3:265‐9. - PMC - PubMed
Burke 1975 {published data only}
Chang 2009 {published and unpublished data}
Childers 1996 {published data only}
-
- Childers MK, Stacy M, Cooke DL, Stonnington HH. Comparison of two injection techniques using botulinum toxin in spastic hemiplegia. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 1996; Vol. 75, issue 6:462‐9. - PubMed
Cocchiarella 1967 {published data only}
-
- Cocchiarella A, Downey JA, Darling RC. Evaluation of the effect of diazepam on spasticity. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1967; Vol. 48, issue 8:393‐6. - PubMed
Cohan 1980 {published data only}
-
- Cohan SL, Raines A, Panagakos J, Armitage P. Phenytoin and chlorpromazine in the treatment of spasticity. Archives of Neurology 1980; Vol. 37, issue 6:360‐4. - PubMed
Copley 2013 {published data only}
-
- Copley J, Kuipers K, Fleming J, Rassafiani M. Individualised resting hand splints for adults with acquired brain injury: a randomized, single blinded, single case design. Neurorehabilitation 2013;32:885‐98. - PubMed
Corry 1998 {published data only}
-
- Corry IS, Cosgrove AP, Duffy CM, McNeill S, Taylor TC, Graham HK. Botulinum toxin A compared with stretching casts in the treatment of spastic equinus: a randomised prospective trial. Journal of Pediatric Orthopedics. 1998/05/26 1998; Vol. 18, issue 3:304‐11. - PubMed
Fazekas 2007 {published data only}
-
- Fazekas G, Horvath M, Troznai T, Toth A. Robot‐mediated upper limb physiotherapy for patients with spastic hemiparesis: a preliminary study. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine 2007; Vol. 39, issue 7:580‐2. [1650‐1977] - PubMed
Fietzek 2014 {published data only}
-
- Fietzek UM, Kossmehl P, Schelosky L, Ebersbach G, Wissel J. Early botulinum toxin treatment for spastic pes equinovarus ‐ a randomized double‐blind placebo‐controlled study. European Journal of Neurology 2014;21:1089‐95. - PubMed
Francisco 2002 {published data only}
-
- Francisco GE, Boake C, Vaughn A. Botulinum toxin in upper limb spasticity after acquired brain injury: a randomized trial comparing dilution techniques. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2002; Vol. 81, issue 5:355‐63. - PubMed
Gracies 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gracies JM, Lugassy M, Weisz DJ, Vecchio M, Flanagan S, Simpson DM. Botulinum toxin dilution and endplate targeting in spasticity: a double‐blind controlled study. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2009; Vol. 90, issue 1:9‐16. - PubMed
-
- Gracies JM, Weisz DJ, Yang BY, Flanagan S, Simpson DM. Impact of botulinum toxin type A (BTX‐A) dilution and endplate targeting technique in upper limb spasticity (abstract). Annals of Neurology 2002;52(Suppl 3):S87.
Grazko 1995 {published data only}
-
- Grazko MA, Polo KB, Jabbari B. Botulinum toxin A for spasticity, muscle spasms, and rigidity. Neurology. 1995/04/01 1995; Vol. 45, issue 4:712‐7. [0028‐3878: (Print)] - PubMed
Guo 2006 {published data only}
-
- Guo F, Yue W, Ren L, Zhang YM, Yang J. Botulinum toxin type A plus rehabilitative training for improving the motor function of the upper limbs and activities of daily life in patients with stroke and brain injury. Neural Regeneration Research 2006; Vol. 1, issue 9:859‐61.
Harvey 1974 {published data only}
-
- Harvey MS, Knight JDS, Lal R, Stockley AGI, Timney AP, White CJ, et al. A comparative trial of dimethothiazine in spastic conditions. A report from the General Practitioner Research Group. Practitioner 1974; Vol. 213, issue 1273:101‐5. - PubMed
Harvey 2006 {published data only}
-
- Harvey L, Jong I, Goehl G, Mardwedel S. Twelve weeks of nightly stretch does not reduce thumb web‐space contractures in people with a neurological condition: a randomised controlled trial. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy 2006;52(4):251‐8. - PubMed
Hill 1994 {published data only}
-
- Hill J. The effects of casting on upper extremity motor disorders after brain injury. American Journal of Occupational Therapy 1994; Vol. 48, issue 3:219‐24. - PubMed
Imle 1986 {published data only}
-
- Imle PC, Eppinghaus CE, Boughton AC. Efficacy of non‐bivalved and bivalved serial casting on head injured patients in intensive care. Physical Therapy 1986; Vol. 66:748 (abstract).
Krewer 2014 {published data only}
-
- Krewer C, Hartl S, Müller F, Koenig E. Effects of repetitive peripheral magnetic stimulation on upper‐limb spasticity and impairment in patients with spastic hemiparesis: a randomized, double‐blind, sham‐controlled study. Archives of Physical and Medical Rehabilitation 2014;95:1039‐47. - PubMed
Lannin 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lannin NA, Horsley SA, Herbert R, McCuskey A, Cusiek A. Splinting the hand in the functional position after brain impairment: a randomized, controlled trial. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2003; Vol. 84, issue 2:297‐302. - PubMed
Leung 2012 {published data only}
-
- Leung J, Harvey LA, Moseley AM, Tse C, Bryant J, Wyndham S, et al. Electrical stimulation and splinting were not clearly more effective than splinting alone for contracture management after acquired brain injury: a randomised trial. Journal of Physiotherapy 2012;58:231‐40. - PubMed
Levine 1969 {published data only}
-
- Levine IM, Jossmann PB, Friend DG, DeAngelis V. Prazepam in the treatment of spasticity. A quantitative double‐blind evaluation. Neurology 1969; Vol. 19, issue 5:510‐6. - PubMed
Levine 1977 {published data only}
-
- Levine IM, Jossmann PB, DeAngelis V. Liorseal, a new muscle relaxant in the treatment of spasticity ‐ a double‐blind quantitative evaluation. Diseases of the Nervous System 1977; Vol. 38, issue 12:1011‐5. - PubMed
Mancini 2005 {published data only}
-
- Mancini F, Sandrini G, Moglia A, Nappi G, Pacchetti C. A randomised, double‐blind, dose‐ranging study to evaluate efficacy and safety of three doses of botulinum toxin type A (Botox) for the treatment of spastic foot. Neurological Sciences 2005; Vol. 26, issue 1:26‐31. [1590‐1874] - PubMed
Martin 2014 {published data only}
Mayer 2008 {published data only}
-
- Mayer NH, Whyte J, Wannstedt G, Ellis CA. Comparative impact of 2 botulinum toxin injection techniques for elbow flexor hypertonia. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2008; Vol. 89, issue 5:982‐7. - PubMed
McPherson 1982 {published data only}
-
- McPherson JJ, Kreimeyer D, Aalderks M, Gallagher T. A comparison of dorsal and volar resting hand splints in the reduction of hypertonus. American Journal of Occupational Therapy 1982; Vol. 36, issue 10:664‐70. - PubMed
Meythaler 2001b {published data only}
-
- Meythaler JM, Guin‐Renfroe S, Johnson A, Brunner RM. Prospective assessment of tizanidine for spasticity due to acquired brain injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2001; Vol. 82, issue 9:1155‐63. - PubMed
Middel 1997 {published data only}
-
- Middel B, KuipersUpmeijer H, Bouma J, Staal M, Oenema D, Postma T, et al. Effect of intrathecal baclofen delivered by an implanted programmable pump on health related quality of life in patients with severe spasticity. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 1997; Vol. 63, issue 2:204‐9. - PMC - PubMed
Moseley 1997 {published data only}
-
- Moseley AM. The effect of casting combined with stretching on passive ankle dorsiflexion in adults with traumatic head injuries. Physical Therapy 1997; Vol. 77, issue 3:240‐7. [0031‐9023: (Print)] - PubMed
Moseley 2008 {published data only}
-
- Moseley AM, Hassett LM, Leung J, Clare JS, Herbert RD, Harvey LA. Serial casting versus positioning for the treatment of elbow contractures in adults with traumatic brain injury: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical Rehabilitation 2008; Vol. 22, issue 5:406‐17. - PubMed
Nakhostin 2009 {published data only}
-
- Nakhostin Ansari N, Naghdi S, Hasson S, Rastgoo M. Efficacy of therapeutic ultrasound and infrared in the management of muscle spasticity. Brain Injury 2009; Vol. 23, issue 7‐8:632‐8. - PubMed
NCT00776048 {published data only}
-
- NCT00776048. Validation of an obstacle course used in patients with muscle tightness. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT00776048 Date first received: 20 October 2008.
NCT00900666 {published data only}
-
- NCT00900666. Efficacy of botulinum toxin Injections in the rectus femoris to treat stiff knee gait following acquired brain injury. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00900666 Date first received: 13 May 2009.
Pagano 1990 {published data only}
-
- Pagano MA, Frerreiro ME, Herskovits. Study using Tizanidina and Baclofen in patients with chronic spasticity. Revista Neurológica Argentina 1990; Vol. 15, issue 1:27‐33.
Penn 1988 {published data only}
-
- Penn RD. Intrathecal baclofen for severe spasticity. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1988; Vol. 531:157‐66. - PubMed
Richardson 2000 {published data only}
Roussan 1985 {published data only}
-
- Roussan M, Terrence C, Fromm G. Baclofen versus diazepam for the treatment of spasticity and long‐term follow‐up of baclofen therapy. Pharmatherapeutica 1985; Vol. 4, issue 5:278‐84. - PubMed
Sahuquillo 2000 {published data only}
-
- Sahuquillo J, Robles A, Poca A, Ballabriga A, Mercadal J, Secades JJ. A controlled, double‐blind, randomized pilot clinical trial of nicardipine as compared with a placebo in patients with moderate or severe head injury. Revista de Neurologia 2000; Vol. 30, issue 5:401‐8. - PubMed
Simpson 1996 {published data only}
-
- Simpson DM, Alexander DN, O'Brien CF, Tagliati M, Aswad AS, Leon JM, et al. Botulinum toxin type A in the treatment of upper extremity spasticity: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Neurology 1996; Vol. 46, issue 5:1306‐10. - PubMed
Simpson 2009 {published data only}
-
- Simpson DM, Gracies JM, Yablon SA, Barbano R, Brashear A, BoNT/TZD Study Team. Botulinum neurotoxin versus tizanidine in upper limb spasticity: a placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 2009; Vol. 80, issue 4:380‐5. - PubMed
Smith 2000 {published data only}
-
- Smith SJ, Ellis E, White S, Moore AP. A double‐blind placebo‐controlled study of botulinum toxin in upper limb spasticity after stroke or head injury. Clinical Rehabilitation 2000; Vol. 14, issue 1:5‐13. - PubMed
Snow 1990 {published data only}
-
- Snow BJ, Tsui JK, Bhatt MH, Varelas M, Hashimoto SA, Calne DB. Treatment of spasticity with botulinum toxin: a double‐blind study. Annals of Neurology 1990; Vol. 28, issue 4:512‐5. [0364‐5134: (Print)] - PubMed
Suputtitada 2005 {published data only}
-
- Suputtitada A, Suwanwela NC. The lowest effective dose of botulinum A toxin in adult patients with upper limb spasticity. Disability & Rehabilitation 2005; Vol. 27, issue 4:176‐84. - PubMed
Thibaut 2015 {published data only}
-
- Thibaut A, Deltombe T, Wannez S, Gosseries O, Ziegler E, Dieni C, et al. Impact of soft splints on upper limb spasticity in chronic patients with disorders of consciousness: a randomized, single‐blind, controlled trial. Brain Injury 2015;29:830‐6. - PubMed
Van Schaeybroeck 2000 {published data only}
-
- Schaeybroeck P, Nuttin B, Lagae L, Schrijvers E, Borghgraef C, Feys P. Intrathecal baclofen for intractable cerebral spasticity: a prospective placebo‐controlled, double‐blind study. Neurosurgery 2000; Vol. 46, issue 3:603‐9. - PubMed
Yelnik 2007 {published data only}
-
- Yelnik AP, Colle FM, Bonan IV, Vicaut E. Treatment of shoulder pain in spastic hemiplegia by reducing spasticity of the subscapular muscle: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study of botulinum toxin A. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 2007; Vol. 78, issue 8:845‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Zhao 2015 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
2009‐015868‐34 {published data only}
-
- A phase III, multicentre, double‐blind, prospective, randomized, placebo‐controlled study, assessing the efficacy and safety of Dysport® used for the treatment of lower‐limb spasticity in adult subjects with hemiparesis due to stroke or traumatic brain injury. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/search?query=eudract_number:200... Date first received: 15 February 2011.
EUCTR2011‐005375‐16‐SE {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- A phase III prospective, multi‐center, randomised evaluator‐blinded study to compare neuromuscular junction (NMJ) targeted technique for Dysport injectives in upper limb spasticity post stroke or traumatic brain injury to the technique used in clinical practice. www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/trial/2011‐005375‐16/results Date first received: 24 September 2012.
Gracies 2016 {published data only}
-
- Gracies JM, Esquenazi A, Brashear A, Edgley SR, O'Dell M, Hedera P, et al. Poster 288. Efficacy and safety of repeated abobotulinumtoxinA injections in adults with lower limb spasticity. PM & R : the Journal of Injury, Function, and Rehabilitation 2016;8:S254. - PubMed
-
- Ipsen. Dysport® adult lower limb spasticity follow‐on study. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01251367 Date first received: 1 December 2010.
IRCT2014041112777N {published data only}
-
- Rasras S. Comparative efficacy of cyproheptadine and baclofen on spasticity in patients with head trauma. en.search.irct.ir/view/17738 Date first received: 13 May 2014.
-
- Rasras S, Fallahpour S, Zeinali M, Soltani A, Bahrami R, Teymoori AR, et al. Survey effect of cyproheptadine‐baclofen and cyproheptadine baclofen‐thizanidine regimens on spasticity in patients with traumatic brain injury. Asian Journal of Medical and Pharmaceutical Researches 2014;4:142‐6.
NCT02052024 {published data only}
-
- NCT02052024. Myobloc atrophy study (MAS). Clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02052024 Date first received: 31 January 2014.
References to ongoing studies
ACTRN12615000821594 {published data only}
-
- ACTRN12615000821594. Effectiveness of combining serial casting and botulinum toxin for the management of ankle contractures after traumatic brain injury: a randomised controlled study. www.anzctr.org.au/Trial/Registration/TrialReview.aspx?id=365685 Date first received: 10 August 2015.
Additional references
Ada 2006a
-
- Ada L, O'Dwyer N, O'Neill E. Relation between spasticity, weakness and contracture of the elbow flexors and upper limb activity after stroke: an observational study. Disability and Rehabilitation 2006; Vol. 28, issue 13‐14:891‐7. - PubMed
Ada 2006b
-
- Ada L, Dorsch S, Canning CG. Strengthening interventions increase strength and improve activity after stroke: a systematic review. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy 2006; Vol. 52, issue 4:241‐8. - PubMed
Ade‐Hall 2000
Allison 1995
-
- Allison SC, Abraham LD. Correlation of quantitative measures with the modified Ashworth Scale in the assessment of plantar flexor spasticity in patients with traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurology 1995; Vol. 242, issue 10:699‐706. - PubMed
Amatya 2013
Ashworth 2012
-
- Ashworth NL, Satkunam LE, Deforge D. Treatment for spasticity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/motor neuron disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004156.pub4] - DOI
Aydin 2005
-
- Aydin G, Tomruk S, Keleş I, Demir S, Orkun S. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation versus baclofen in spasticity: clinical and electrophysiologic comparison. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2005; Vol. 84, issue 8:584‐92. [0894‐9115] - PubMed
Baker 2015
-
- Baker JA, Pereira G. The efficacy of botulinum toxin A on improving ease of care in the upper and lower limbs: a systematic review and meta‐analysis using the Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation approach. Clinical Rehabilitation 2015;29:731‐40. - PubMed
Becker 1997
-
- Becker R, Alberti O, Bauer BL. Continuous intrathecal baclofen infusion in severe spasticity after traumatic or hypoxic brain injury. Journal of Neurology 1997; Vol. 244, issue 3:160‐6. - PubMed
Bragge 2016
-
- Bragge P, Synnot A, Maas AI, Menon DK, Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, et al. A state of the science overview of randomised controlled trials evaluating acute management of moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neurotrauma 2016;33(16):1461‐78.. [DOI: 10.1089/neu.2015.4233] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Brashear 2002
-
- Brashear A, Zafonte R, Corcoran M, Galvez‐Jimenez N, Gracies JM, Gordon MF, et al. Inter‐ and intrarater reliability of the Ashworth Scale and the Disability Assessment Scale in patients with upper‐limb poststroke spasticity. Archives of Physical and Medical Rehabilitation 2002;83:1349‐54. - PubMed
Brashear 2016
-
- Brashear A, Elovic E. Why is spasticity important?. Spasticity: Diagnosis and Management. New York (NY): Demos Medical Publishing, 2016:3‐4.
Brazinova 2016
Dashtipour 2016
Demetrios 2013
-
- Demetrios M, Khan F, Turner‐Stokes L, Brand C, McSweeney S. Multidisciplinary rehabilitation following botulinum toxin and other focal intramuscular treatment for post‐stroke spasticity. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009689.pub2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Dong 2017
-
- Dong Y, Wu T, Hu X, Wang T. Efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin type A for upper limb spasticity after stroke or traumatic brain injury: a systematic review with meta‐analysis and trial sequential analysis. European Journal of Physical Rehabilitation Medicine 2017;53:256‐67. - PubMed
Duarte 2016
Esquenazi 2006
-
- Esquenazi A. Improvements in healthcare and cost benefits associated with botulinum toxin treatment of spasticity and muscle overactivity. European Journal of Neurology 2006; Vol. 13 (Suppl 4):27‐34. - PubMed
Fleuren 2010
-
- Fleuren JFM, Voerman GE, Erren‐Wolters CV, Snoek GJ, Rietman JS, Hermens HJ, et al. Stop using the Ashworth Scale for the assessment of spasticity. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 2010; Vol. 81, issue 1:46‐52. - PubMed
Francis 2004
Giovannelli 2007
-
- Giovannelli M, Borriello G, Castri P, Prosperini L, Pozzilli C. Early physiotherapy after injection of botulinum toxin increases the beneficial effects on spasticity in patients with multiple sclerosis. Clinical Rehabilitation. London: SAGE PUBLICATIONS, INC., 2007; Vol. 21, issue 4:331‐7. [02692155] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso‐Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence ‐ imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64:1283‐93. - PubMed
Hall 1993
-
- Hall KM, Hamilton BB, Gordon WA, Zasler ND. Characteristics and comparisons of functional assessment indices: disability rating scale, functional independence measure, and functional assessment measure. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation 1993;8:60‐74.
Haugh 2006
-
- Haugh AB, Pandyan AD, Johnson GR. A systematic review of the Tardieu Scale for the measurement of spasticity. Disability and Rehabilitation 2006; Vol. 28, issue 15:899‐907. - PubMed
Higgins 2011
Hoare 2010
-
- Hoare BJ, Wallen MA, Imms C, Villanueva E, Rawicki HB, Carey L. Botulinum toxin A as an adjunct to treatment in the management of the upper limb in children with spastic cerebral palsy (update). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003469.pub4] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Hsieh 2012
-
- Hsieh JTC, Wolfe DL, McIntyre A, Janzen S, Townson AF, Short C, et al. Spasticity following spinal cord injury. In: Eng JJ, Teasell RW, Miller WC, Wolfe DL, Townson AF, Hsieh JTC, et al. editor(s). Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Evidence, Version 4.0. Vancouver (BC): SCIRE Project, 2012.
Jennett 1975
-
- Jennett B, Bond M. Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. Lancet 1975;1:480‐4. - PubMed
Keith 1987
-
- Keith RA, Granger CV, Hamilton BB, Sherwin FS. The functional independence measure: a new tool for rehabilitation. Advances in Clinical Rehabilitation 1987;1:6‐18. - PubMed
Khan 2003
-
- Khan F, Baguley IJ, Cameron ID. Rehabilitation after traumatic brain injury. Medical Journal of Australia. 2003/03/14 2003; Vol. 178, issue 6:290‐5. - PubMed
Kiresuk 1994
-
- Kiresuk TJ, Smith A, Cardillo JE. Goal Attainment Scaling: Applications, Theory, and Measurement. Hillsdale (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1994.
Kwakkel 1999
-
- Kwakkel G, Wagenaar R, Twisk J, Lankhorst G, Koetsier J. Intensity of leg and arm training after primary middle‐cerebral‐artery stroke: a randomised trial. Lancet 1999; Vol. 354:191‐6. - PubMed
Lance 1980
-
- Lance J. Pathophysiology of spasticity and clinical experience with baclofen. In: Lance JWFR, Young RR, Koella WP editor(s). Spasticity: Disordered Motor Control. Chicago (IL): Year Book Medical Publishers, 1980.
Law 2000
-
- Law M, Baptiste S, Carswell A, McColl MA, Polatajko H, Pollock N. Canadian Occupational Performance Measure. Canada: CAOT Publications, 2000.
Lindsay 2013
Maas 2008
-
- Maas AI, Stocchetti N, Bullock R. Moderate and severe traumatic brain injury in adults. Lancet Neurology. 2008/07/19 2008; Vol. 7, issue 8:728‐41. - PubMed
Maas 2010
Malhotra 2009
-
- Malhotra S, Pandyan AD, Day CR, Jones PW, Hermens H. Spasticity, an impairment that is poorly defined and poorly measured. Clinical Rehabilitation 2009;23:651‐8. - PubMed
Manchester 1997
-
- Manchester D, Hodgkinson A, Casey T. Prolonged, severe behavioural disturbance following traumatic brain injury: what can be done?. Brain Injury 1997;11:605‐17. - PubMed
McGuire 2016
-
- McGuire J. Epidemiology of spasticity in the adult and child. In: Brashear A editor(s). Spasticity: Diagnosis and Management. 2nd Edition. New York (NY): Demos Medical Publishing, 2016.
Mehrholz 2005
-
- Mehrholz J, Major Y, Meissner D, Sandi‐Gahun S, Koch R, Pohl M. The influence of contractures and variation in measurement stretching velocity on the reliability of the Modified Ashworth Scale in patients with severe brain injury. Clinical Rehabilitation 2005; Vol. 19, issue 1:63‐72. - PubMed
Meythaler 2001a
-
- Meythaler JM, Guin‐Renfroe S, Johnson A, Brunner RM. Prospective assessment of tizanidine for spasticity due to acquired brain injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2001; Vol. 82, issue 9:1155‐63. - PubMed
Morris 2002
-
- Morris S. Ashworth and Tardieu Scales: their Clinical Relevance for Measuring Spasticity in Adult and Paediatric Neurological Populations. Physical Therapy Reviews 2002; Vol. 7, issue 1:53‐62.
Mortenson 2003
-
- Mortenson PA, Eng JJ. The use of casts in the management of joint mobility and hypertonia following brain injury in adults: a systematic review. Physical Therapy 2003;83:648‐58. - PubMed
Nair 2014
-
- Nair KPS, Marsden J. The management of spasticity in adults. BMJ 2014;349:g4737. - PubMed
O'Dell 2015
-
- O'Dell MW, Walker HW, Edgley SR, Gracies JM, Gul F, Wimmer M, et al. AbobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport®) in the treatment of adult patients with upper limb spasticity due to traumatic brain injury. PM & R : the Journal of Injury, Function, and Rehabilitation 2015;7:S103.
Olver 2010
-
- Olver J, Esquenazi A, Fung VSC, Singer BJ, Ward AB. Botulinum toxin assessment, intervention and aftercare for lower limb disorders of movement and muscle tone in adults: international consensus statement. European Journal of Neurology 2010;17:57‐73. - PubMed
Pandyan 1999
-
- Pandyan AD, Johnson GR, Price CI, Curless RH, Barnes MP, Rodgers H. A review of the properties and limitations of the Ashworth and modified Ashworth Scales as measures of spasticity. Clinical Rehabilitation 1999; Vol. 13, issue 5:373‐83. - PubMed
Pandyan 2005
-
- Pandyan A, Gregoric M, Barnes M, Wood D, Wijck F, Burridge J, et al. Spasticity: clinical perceptions, neurological realities and meaningful measurement. Disability and Rehabilitation 2005; Vol. 27:2‐6. - PubMed
Parke 1989
-
- Parke B, Penn RD, Savoy SM, Corcos D. Functional outcome after delivery of intrathecal baclofen. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1989; Vol. 70, issue 1:30‐2. - PubMed
Patrick 2006
-
- Patrick E, Ada L. The Tardieu Scale differentiates contracture from spasticity whereas the Ashworth Scale is confounded by it. Clinical Rehabilitation 2006;20:173‐82. - PubMed
Pierson 1996
-
- Pierson SH, Katz DI, Tarsy D. Botulinum toxin A in the treatment of spasticity: functional implications and patient selection. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 1996; Vol. 77, issue 7:717‐21. - PubMed
RCP 2009
-
- Royal College of Physicians. Spasticity in Adults: Management using Botulinum Toxin: National Guidelines. London (UK): Royal College of Physicians, 2009.
RevMan 2011 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011.
Ryan 2016
-
- Ryan R, Hill S. How to GRADE the quality of the evidence. Cochrane Consumers and Communication Group, Version 3.0 December 2016. cccrg.cochrane.org/sites/cccrg.cochrane.org/files/public/uploads/how_to_... (accessed prior to 25 October 2017).
Schünemann 2011
-
- Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Guyatt GH. Chapter 11: Presenting results and 'Summary of findings' tables. In: Higgins JP, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Shakespeare 2003
Singer 2004
-
- Singer BJ, Jegasothy GM, Singer KP, Allison GT, Dunne JW. Incidence of ankle contracture after moderate to severe acquired brain injury. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 2004/09/18 2004; Vol. 85, issue 9:1465‐9. - PubMed
Summers 2009
-
- Summers CR, Ivins B, Schwab KA. Traumatic brain injury in the United States: an epidemiologic overview. Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine 2009; Vol. 76, issue 2:105‐10. - PubMed
Taricco 2000
Teasdale 1974
-
- Teasdale G, Jennett B. Assessment of coma and impaired consciousness. Lancet 1974;304:814. - PubMed
Wedekind 2005
-
- Wedekind C, Lippert‐Grüner M. Long‐term outcome in severe traumatic brain injury is significantly influenced by brainstem involvement. Brain Injuries 2005;19:681‐4. - PubMed
WHO 2010
-
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability & Health. apps.who.int/classifications/icfbrowser/ (accessed 2 July 2010).
Williams 2015a
-
- Williams G, Banky M, Olver J. Severity and distribution of spasticity does not limit mobility or influence compensatory strategies following traumatic brain injury. Brain Injury 2015;29(10):1232‐8. - PubMed
Williams 2015b
-
- Williams G, Banky M, Olver J. Distribution of lower limb spasticity does not influence mobility outcome following traumatic brain injury: an observational study. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation 2015;30(5):E49‐57. - PubMed
Wood 1999
-
- Wood RL, McCrea JD, Wood LM, Merriman RN. Clinical and cost effectiveness of post‐acute neurobehavioural rehabilitation. Brain Injury 1999;13:69‐88. - PubMed
Wood 2008
Yelnik 2009
-
- Yelnik AP, Simon O, Bensmail D, Chaleat‐Valayer E, Decq P, Dehail P, et al. Drug treatments for spasticity. Annals of Physical & Rehabilitation Medicine 2009; Vol. 52, issue 10:746‐56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

