Leptomeningeal metastasis from systemic cancer: Review and update on management
- PMID: 29165794
- PMCID: PMC7418844
- DOI: 10.1002/cncr.30911
Leptomeningeal metastasis from systemic cancer: Review and update on management
Abstract
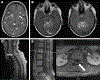
Leptomeningeal metastasis is an uncommon and typically late complication of cancer with a poor prognosis and limited treatment options. Diagnosis is often challenging, with nonspecific presenting symptoms ranging from headache and confusion to focal neurologic deficits, such as cranial nerve palsies. Standard diagnostic evaluation involves a neurologic examination, magnetic resonance imaging of the brain and spine with gadolinium, and cytologic evaluation of the cerebral spinal fluid. Therapy entails a multimodal approach focused on palliation with surgery, radiation, and/or chemotherapy, which may be administered systemically or directly into the cerebral spinal fluid. Limited trial data exist to guide treatment, and current regimens are based primarily on expert opinion. Although newer targeted and immunotherapeutic agents are under investigation and have shown promise, an improved understanding of the biology of leptomeningeal metastasis and treatment resistance as well as additional randomized controlled studies are needed to guide the optimal treatment of this devastating disease. Cancer 2018;124:21-35. © 2017 American Cancer Society.
Keywords: brain metastasis; carcinomatous meningitis; leptomeningeal carcinomatosis; leptomeningeal disease; leptomeningeal metastasis.
© 2017 American Cancer Society.
Figures
References
-
- Eberth CJ. Zur Entwickelung des Epithelioms (Cholesteatoms) der Pia und der Lunge. Arch für Pathol Anat und Physiol und für Klin Med. 1869;49(1):51–63. 10.1007/BF02214196. - DOI
-
- Boyle R, Thomas M, Adams JH. Diffuse involvement of the leptomeninges by tumour--a clinical and pathological study of 63 cases. Postgrad Med J. 1980;56(653):149–158. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7393804. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical