Effective strategies for scaling up evidence-based practices in primary care: a systematic review
- PMID: 29166911
- PMCID: PMC5700621
- DOI: 10.1186/s13012-017-0672-y
Effective strategies for scaling up evidence-based practices in primary care: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: While an extensive array of existing evidence-based practices (EBPs) have the potential to improve patient outcomes, little is known about how to implement EBPs on a larger scale. Therefore, we sought to identify effective strategies for scaling up EBPs in primary care.
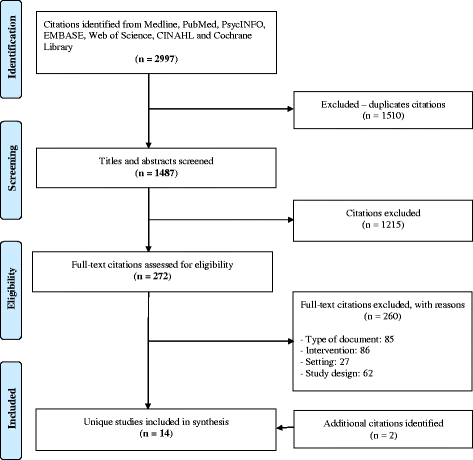
Methods: We conducted a systematic review with the following inclusion criteria: (i) study design: randomized and non-randomized controlled trials, before-and-after (with/without control), and interrupted time series; (ii) participants: primary care-related units (e.g., clinical sites, patients); (iii) intervention: any strategy used to scale up an EBP; (iv) comparator: no restrictions; and (v) outcomes: no restrictions. We searched MEDLINE, Embase, PsycINFO, Web of Science, CINAHL, and the Cochrane Library from database inception to August 2016 and consulted clinical trial registries and gray literature. Two reviewers independently selected eligible studies, then extracted and analyzed data following the Cochrane methodology. We extracted components of scaling-up strategies and classified them into five categories: infrastructure, policy/regulation, financial, human resources-related, and patient involvement. We extracted scaling-up process outcomes, such as coverage, and provider/patient outcomes. We validated data extraction with study authors.
Results: We included 14 studies. They were published since 2003 and primarily conducted in low-/middle-income countries (n = 11). Most were funded by governmental organizations (n = 8). The clinical area most represented was infectious diseases (HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria, n = 8), followed by newborn/child care (n = 4), depression (n = 1), and preventing seniors' falls (n = 1). Study designs were mostly before-and-after (without control, n = 8). The most frequently targeted unit of scaling up was the clinical site (n = 11). The component of a scaling-up strategy most frequently mentioned was human resource-related (n = 12). All studies reported patient/provider outcomes. Three studies reported scaling-up coverage, but no study quantitatively reported achieving a coverage of 80% in combination with a favorable impact.
Conclusions: We found few studies assessing strategies for scaling up EBPs in primary care settings. It is uncertain whether any strategies were effective as most studies focused more on patient/provider outcomes and less on scaling-up process outcomes. Minimal consensus on the metrics of scaling up are needed for assessing the scaling up of EBPs in primary care.
Trial registration: This review is registered as PROSPERO CRD42016041461 .
Keywords: Evidence-based practices; Implementation; Knowledge translation; Primary care; Scaling up; Spread; Systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Fooks C. Implementing primary care reform in Canada: barriers and facilitators [Internet]. School of Policy Studies Queen’s University Kingston. Ontario: McGill-Queen’s University Press; 2003.
-
- Peckham S, Exworthy M. Primary care in the UK: policy, organisation and management. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan; 2003.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources