Visualizing the complex functions and mechanisms of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C)
- PMID: 29167309
- PMCID: PMC5717348
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.170204
Visualizing the complex functions and mechanisms of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C)
Abstract
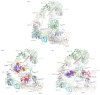
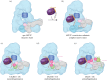
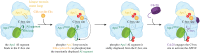
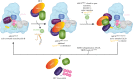
The anaphase promoting complex or cyclosome (APC/C) is a large multi-subunit E3 ubiquitin ligase that orchestrates cell cycle progression by mediating the degradation of important cell cycle regulators. During the two decades since its discovery, much has been learnt concerning its role in recognizing and ubiquitinating specific proteins in a cell-cycle-dependent manner, the mechanisms governing substrate specificity, the catalytic process of assembling polyubiquitin chains on its target proteins, and its regulation by phosphorylation and the spindle assembly checkpoint. The past few years have witnessed significant progress in understanding the quantitative mechanisms underlying these varied APC/C functions. This review integrates the overall functions and properties of the APC/C with mechanistic insights gained from recent cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) studies of reconstituted human APC/C complexes.
Keywords: APC/C; cell cycle; cryo-EM; spindle assembly checkpoint.
© 2017 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures

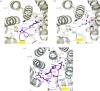
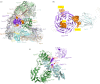
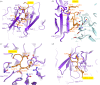
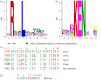
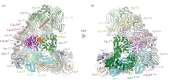

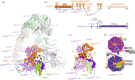

References
-
- Irniger S, Piatti S, Michaelis C, Nasmyth K. 1995. Genes involved in sister chromatid separation are needed for B-type cyclin proteolysis in budding yeast. Cell 81, 269–278. (doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90337-2) - DOI - PubMed
-
- King RW, Peters J-M, Tugendreich S, Rolfe M, Hieter P, Kirschner MW. 1995. A 20S complex containing CDC27 and CDC16 catalyzes the mitosis-specific conjugation of ubiquitin to cyclin B. Cell 81, 279–288. (doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90338-0) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sudakin V, Ganoth D, Dahan A, Heller H, Hershko J, Luca FC, Ruderman JV, Hershko A. 1995. The cyclosome, a large complex containing cyclin-selective ubiquitin ligase activity, targets cyclins for destruction at the end of mitosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 6, 185–197. (doi:10.1091/mbc.6.2.185) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tugendreich S, Tomkiel J, Earnshaw W, Hieter P. 1995. CDC27Hs colocalizes with CDC16Hs to the centrosome and mitotic spindle and is essential for the metaphase to anaphase transition. Cell 81, 261–268. (doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90336-4) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herrero-Mendez A, Almeida A, Fernández E, Maestre C, Moncada S, Bolaños JP. 2009. The bioenergetic and antioxidant status of neurons is controlled by continuous degradation of a key glycolytic enzyme by APC/C-Cdh1. Nat. Cell Biol. 11, 747–752. (doi:10.1038/ncb1881) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
