Genetic variants in the platelet-derived growth factor subunit B gene associated with pancreatic cancer risk
- PMID: 29168174
- PMCID: PMC5805574
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.31171
Genetic variants in the platelet-derived growth factor subunit B gene associated with pancreatic cancer risk
Abstract
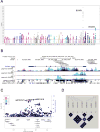
The platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) signaling pathway plays important roles in development and progression of human cancers. In our study, we aimed to identify genetic variants of the PDGF pathway genes associated with pancreatic cancer (PC) risk in European populations using three published genome-wide association study datasets, which consisted of 9,381 cases and 7,719 controls. The expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) analysis was also performed using data from the 1000 Genomes, TCGA and GTEx projects. As a result, we identified two potential susceptibility loci (rs5757573 and rs6001516) of PDGFB associated with PC risk [odds ratio (OR) = 1.10, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.05-1.16, and p = 4.70 × 10-5 for the rs5757573 C allele and 1.21, 1.11-1.32, and 2.01 × 10-5 for the rs6001516 T allele]. Haplotype analysis revealed that the C-T haplotype carriers had a significantly increased risk of PC than those carrying the T-C haplotype (OR = 1.23, 95% CI = 1.12-1.34, p =5.00 × 10-6 ). The multivariate regression model incorporating the number of unfavorable genotypes (NUGs) with age and sex showed that carriers with 1-2 NUGs, particularly among 60-70 age group or males, had an increased risk of PC, compared to those without NUG. Furthermore, the eQTL analysis revealed that both loci were correlated with a decreased mRNA expression level of PDGFB in lymphoblastoid cell lines and pancreatic tumor tissues (p = 0.015 and 0.071, respectively). Our results suggest that genetic variants in PDGFB may play a role in susceptibility to PC. Further population and functional validations of our findings are warranted.
Keywords: genome-wide association study; pancreatic cancer susceptibility; pathway analysis; platelet-derived growth factor; single nucleotide polymorphism.
© 2017 UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Ma J, Siegel R, Jemal A. Pancreatic cancer death rates by race among US men and women, 1970–2009. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105:1694–700. - PubMed
-
- Kamisawa T, Wood LD, Itoi T, Takaori K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 2016;388:73–85. - PubMed
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials