Genomewide association study of HLA alloimmunization in previously pregnant blood donors
- PMID: 29168253
- PMCID: PMC5803399
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.14402
Genomewide association study of HLA alloimmunization in previously pregnant blood donors
Abstract
Background: Alloimmunization through blood transfusion, transplantation, or circulating fetal cells during pregnancy is a significant concern. Some exposed individuals make alloantibodies while others do not, implying variation in genetic risk factors.
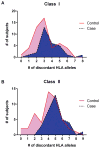
Study design and methods: We conducted a genomewide association study (GWAS) of 9,427,497 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to identify genetic variants for HLA alloimmunization in previously pregnant blood donors with (n = 752) and without (n = 753) HLA Class I or II alloantibodies.
Results: A SNP in the neurexophilin 2 (NXPH2) gene surpassed genome-wide significance (p = 2.06 × 10-8 ), with multiple adjacent markers p < 10-6 , for women with anti-Class I alloantibodies only. Little is currently known about the function of NXPH2, although gene family members have been shown to impact immunity. SNPs in the E2F7 gene, a transcription factor related to cell cycle control and cellular proliferation, also approached genomewide significance (p = 2.5 × 10-7 ).
Conclusion: Further work to extend the GWAS approach and to characterize variants in NXPH2 and E2F7 in the context of alloantibody formation is warranted.
© 2017 AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Payne R. The development and persistence of leukoagglutinins in parous women. Blood. 1962;19:411. - PubMed
-
- Bauer MP, Wiersum-Osselton J, Schipperus M, Vandenbroucke JP, Briët E. Clinical predictors of alloimmunization after red blood cell transfusion. Transfusion. 2007;47:2066. - PubMed
-
- Blumberg N, Heal JM, Gettings KF. WBC reduction of RBC transfusions is associated with a decreased incidence of RBC alloimmunization. Transfusion. 2003;43:945. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL124260/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

