Prognostic value of PD-L1 expression in combination with CD8+ TILs density in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 29168339
- PMCID: PMC5773962
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1243
Prognostic value of PD-L1 expression in combination with CD8+ TILs density in patients with surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
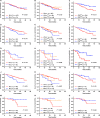
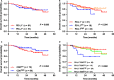
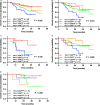
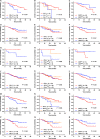
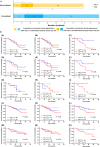
To investigate the prognostic value of PD-L1 expression combined with CD8+ TILs density in patients with resected NSCLC and correlations with clinicopathological features. We retrospectively enrolled 178 patients with resected NSCLC from 2011 to 2015. All surgical primary and 58 matched metastatic lymph node specimens were tested for PD-L1, CD8+ TILs, and oncogenic alterations. PD-L1+ was detected in 71 (39.9%) and CD8high TILs in 74 (41.6%) cases. Smoking, SqCC, and EGFR- were associated with both PD-L1+ and CD8high TILs. Patients with CD8high TILs had longer OS (P = 0.012). PD-L1- was significantly associated with longer OS in patients with oncogenic alterations (P = 0.047). By multivariate analysis, CD8high TILs (HR = 0.411; 95% CI, 0.177-0.954; P = 0.038), rather than PD-L1, was the independent predictive factor for OS. The longest and shortest OS were achieved in patients with PD-L1+ /CD8high and PD-L1+ /CD8low , respectively (P = 0.025). Inconsistent PD-L1 expression levels were observed in 23 of 58 (39.7%) patients with primary and matched metastatic lymph node specimens. Of them, CD8high TILs was significantly associated with longer OS in patients with metastatic lymph nodes and/or consistent PD-L1 expression (P = 0.017 and 0.049, respectively). The combination of PD-L1 and CD8+ TILs density, instead of PD-L1 alone, suggested impressive prognostic values in NSCLC patients. Less than half of patients with resected NSCLC experienced inconsistent PD-L1 expression between primary and metastatic lesions. The level of PD-L1 expression in advanced NSCLC needs to be evaluated more comprehensively.
Keywords: CD8; non-small cell lung cancer; prognosis; programmed cell death ligand-1; tumor infiltrating lymphocytes.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of PD-L1 expression on tumor cells combined with CD8+ TIL density in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Jan 2;15(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1453-3. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31898519 Free PMC article.
-
Expressions of CD8+TILs, PD-L1 and Foxp3+TILs in stage I NSCLC guiding adjuvant chemotherapy decisions.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 27;7(39):64318-64329. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11793. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27602763 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) expression combined with CD8 tumor infiltrating lymphocytes density in non-small cell lung cancer patients.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2018 Dec;30(4):125-131. doi: 10.1016/j.jnci.2018.08.003. Epub 2018 Oct 15. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2018. PMID: 30337185
-
Association between CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2023 Jun;23(6):643-659. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2023.2208351. Epub 2023 May 4. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2023. PMID: 37114477
-
Prognostic Significance of CD4+ Tumour Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Receiving PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors Therapy.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2025 Mar;35(3):341-350. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2025.03.341. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2025. PMID: 40055170
Cited by
-
Combined Immunoscore for Prognostic Stratification of Early Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Sep 25;10:564915. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.564915. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33072595 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Microenvironment of NSCLC based on CD8+ TIL Density and PD-1/PD-L1 Expression.J Cancer. 2019 Jan 1;10(1):211-222. doi: 10.7150/jca.26444. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30662542 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of PD-L1 expression and CD8+ TILs density for disease-free survival in surgically resected lung squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective study.J Thorac Dis. 2022 Jun;14(6):2224-2234. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-630. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35813758 Free PMC article.
-
Sources of inter-individual variability leading to significant changes in anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 efficacy identified in mouse tumor models using a QSP framework.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 5;13:1056365. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1056365. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36545310 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of PD-L1 expression on tumor cells combined with CD8+ TIL density in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy.Radiat Oncol. 2020 Jan 2;15(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1453-3. Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31898519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre, L. A. , Bray F., Siegel R. L., Ferlay J., Lortet‐Tieulent J., and Jemal A.. 2015. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Reck, M. , Rodriguez‐Abreu D., Robinson A. G., Hui R., Csoszi T., Fulop A., et al. 2016. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD‐L1‐positive non‐small‐cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 375:1823–1833. - PubMed
-
- Hegde, P. S. , Karanikas V., and Evers S.. 2016. The where, the when, and the how of immune monitoring for cancer immunotherapies in the era of checkpoint inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 22:1865–1874. - PubMed
-
- Chen, D. S. , and Mellman I.. 2013. Oncology meets immunology: the cancer‐immunity cycle. Immunity 39:1–10. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

