Genomic risk prediction of aromatase inhibitor-related arthralgia in patients with breast cancer using a novel machine-learning algorithm
- PMID: 29168353
- PMCID: PMC5773952
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.1256
Genomic risk prediction of aromatase inhibitor-related arthralgia in patients with breast cancer using a novel machine-learning algorithm
Abstract
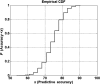
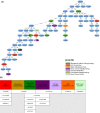
Many breast cancer (BC) patients treated with aromatase inhibitors (AIs) develop aromatase inhibitor-related arthralgia (AIA). Candidate gene studies to identify AIA risk are limited in scope. We evaluated the potential of a novel analytic algorithm (NAA) to predict AIA using germline single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) data obtained before treatment initiation. Systematic chart review of 700 AI-treated patients with stage I-III BC identified asymptomatic patients (n = 39) and those with clinically significant AIA resulting in AI termination or therapy switch (n = 123). Germline DNA was obtained and SNP genotyping performed using the Affymetrix UK BioBank Axiom Array to yield 695,277 SNPs. SNP clusters that most closely defined AIA risk were discovered using an NAA that sequentially combined statistical filtering and a machine-learning algorithm. NCBI PhenGenI and Ensemble databases defined gene attribution of the most discriminating SNPs. Phenotype, pathway, and ontologic analyses assessed functional and mechanistic validity. Demographics were similar in cases and controls. A cluster of 70 SNPs, correlating to 57 genes, was identified. This SNP group predicted AIA occurrence with a maximum accuracy of 75.93%. Strong associations with arthralgia, breast cancer, and estrogen phenotypes were seen in 19/57 genes (33%) and were functionally consistent. Using a NAA, we identified a 70 SNP cluster that predicted AIA risk with fair accuracy. Phenotype, functional, and pathway analysis of attributed genes was consistent with clinical phenotypes. This study is the first to link a specific SNP/gene cluster to AIA risk independent of candidate gene bias.
Keywords: SNP; Aromatase; arthralgia; breast cancer; estrogen; joint pain.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic determinants of aromatase inhibitor-related arthralgia: the B-ABLE cohort study.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 Jul;140(2):385-95. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2638-3. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23868189
-
Patterns and risk factors associated with aromatase inhibitor-related arthralgia among breast cancer survivors.Cancer. 2009 Aug 15;115(16):3631-9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24419. Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19517460 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and genetic risk factors for aromatase inhibitor-associated arthralgia in breast cancer survivors.Breast. 2020 Feb;49:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2019.10.008. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Breast. 2020. PMID: 31678641 Free PMC article.
-
Aromatase inhibitor-induced arthralgia: a review.Ann Oncol. 2013 Jun;24(6):1443-9. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt037. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Ann Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23471104 Review.
-
Effect of acupuncture on aromatase inhibitor-induced arthralgia in patients with breast cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Breast. 2017 Jun;33:132-138. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2017.03.015. Epub 2017 Apr 4. Breast. 2017. PMID: 28384564 Review.
Cited by
-
Robust pathway sampling in phenotype prediction. Application to triple negative breast cancer.BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 Mar 11;21(Suppl 2):89. doi: 10.1186/s12859-020-3356-6. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020. PMID: 32164540 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning techniques for personalized breast cancer risk prediction: comparison with the BCRAT and BOADICEA models.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 20;21(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1158-4. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31221197 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based lifetime breast cancer risk reclassification compared with the BOADICEA model: impact on screening recommendations.Br J Cancer. 2020 Sep;123(5):860-867. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0937-0. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Br J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32565540 Free PMC article.
-
Innovations in Genomics and Big Data Analytics for Personalized Medicine and Health Care: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 22;23(9):4645. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094645. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Survey on the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Biobanking Studies: A Systematic Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 May 9;12(5):1179. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051179. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626333 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pagani, O. , Regan M. M., and Francis P. A.. 2014. Investigators TaS, group IBCS. Exemestane with ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 371:1358–1359. - PubMed
-
- Francis, P. A. , Regan M. M., and Fleming G. F.. 2015. Adjuvant ovarian suppression in premenopausal breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 372:1673. - PubMed
-
- Aydiner, A. . 2013. Meta‐analysis of breast cancer outcome and toxicity in adjuvant trials of aromatase inhibitors in postmenopausal women. Breast (Edinburgh, Scotland) 22:121–129. - PubMed
-
- Niravath, P. 2013. Aromatase inhibitor‐induced arthralgia: a review. Ann. Oncol. 24:1443–1449. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

