Diagnostic value of trait antinuclear antibodies and multiple immunoglobulin production in autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 29168582
- PMCID: PMC6817004
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22361
Diagnostic value of trait antinuclear antibodies and multiple immunoglobulin production in autoimmune diseases
Abstract
Background: Our article aims to evaluate the proportion of monospecific antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and polyclonal ANAs in patients with autoimmune diseases based on the results of an ANA panel and to evaluate the efficiency of trait ANAs as a novel diagnostic tool. This study also aims to investigate immunoglobulin production in autoimmune diseases by detecting different antibodies.
Methods: The serum ANA profile of 634 patients with autoimmune diseases was analyzed using the immunoblot method. A specific formula was developed in an effort to calculate the theoretical proportion of monospecific ANA (TPM) in different disease groups. Different IgM, IgG, and IgE variants for several pathologies were detected.
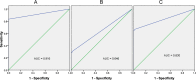
Results: The observed proportions of monospecific ANAs (OPM) were all lower than the predicted TPM in autoimmune diseases. Polyclonal ANAs were predominant in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). There were statistical differences in OPM and TPM in all disease groups (P < .001). Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC curve) analysis of trait ANAs between the SLE group and the control groups indicated an area under the curve of 0.916. Differences were found in IgM of Toxoplasma gondii (TOXO) and IgG of hepatitis C virus (HCV) and Treponema pallidum (TP) when comparing the various disease groups to the control group.
Conclusion: The higher TPM suggests that polyclonal differentiation is the major mechanism of ANA in autoimmune diseases. Trait ANA is potentially a valuable new index for diagnosis in SLE. Further investigation is needed to understand the link between B-cell differentiation and autoimmune diseases.
Keywords: antinuclear antibody; autoimmune disease; immunoglobulin; trait ANA.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of cyclin A as a molecular target of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) in hepatic and non-hepatic autoimmune diseases.J Hepatol. 1996 Dec;25(6):859-66. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(96)80290-x. J Hepatol. 1996. PMID: 9007714
-
The evaluation of cellular immune function in elderly patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Korean J Intern Med. 2019 Jul;34(4):932-937. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2017.224. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Korean J Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 29172398 Free PMC article.
-
Antinuclear antibodies in infectious diseases.Infect Dis (Lond). 2020 Mar;52(3):177-185. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2019.1690676. Epub 2019 Nov 12. Infect Dis (Lond). 2020. PMID: 31718355
-
Clinical utility of antinuclear antibody tests in children.BMC Pediatr. 2004 Jul 9;4:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-4-13. BMC Pediatr. 2004. PMID: 15245579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Modern look at the problems of investigation of antinuclear antibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus (literature review).].Klin Lab Diagn. 2018;63(6):340-348. doi: 10.18821/0869-2084-2018-63-6-340-348. Klin Lab Diagn. 2018. PMID: 30702224 Review. Russian.
References
-
- Margery‐Muir AA, Bundell C, Nelson D, Groth DM, Wetherall JD. Gender balance in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16:258‐268. - PubMed
-
- Dooley MA, Hogan SL. Environmental epidemiology and risk factors for autoimmune disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003;15:99‐103. - PubMed
-
- Javierre BM, Hernando H, Ballestar E. Environmental triggers and epigenetic deregulation in autoimmune disease. Discov Med. 2011;12:535‐545. - PubMed
-
- Alzabin S, Venables PJ. Etiology of autoimmune disease: past, present and future. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2012;8:111‐113. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

