A Bioinformatic Pipeline for Monitoring of the Mutational Stability of Viral Drug Targets with Deep-Sequencing Technology
- PMID: 29168754
- PMCID: PMC5744132
- DOI: 10.3390/v9120357
A Bioinformatic Pipeline for Monitoring of the Mutational Stability of Viral Drug Targets with Deep-Sequencing Technology
Abstract
The efficient development of antiviral drugs, including efficient antiviral small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), requires continuous monitoring of the strict correspondence between a drug and the related highly variable viral DNA/RNA target(s). Deep sequencing is able to provide an assessment of both the general target conservation and the frequency of particular mutations in the different target sites. The aim of this study was to develop a reliable bioinformatic pipeline for the analysis of millions of short, deep sequencing reads corresponding to selected highly variable viral sequences that are drug target(s). The suggested bioinformatic pipeline combines the available programs and the ad hoc scripts based on an original algorithm of the search for the conserved targets in the deep sequencing data. We also present the statistical criteria for the threshold of reliable mutation detection and for the assessment of variations between corresponding data sets. These criteria are robust against the possible sequencing errors in the reads. As an example, the bioinformatic pipeline is applied to the study of the conservation of RNA interference (RNAi) targets in human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) subtype A. The developed pipeline is freely available to download at the website http://virmut.eimb.ru/. Brief comments and comparisons between VirMut and other pipelines are also presented.
Keywords: bioinformatic pipeline; data processing; deep-sequencing; drug targets; mutations; viruses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

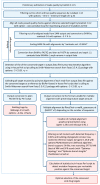
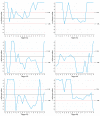
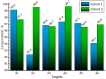
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

