Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and inhibitors
- PMID: 29169144
- PMCID: PMC5745276
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.11.002
Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in cancer: Update on effectors and inhibitors
Abstract
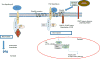
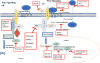
The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is a family of proteins that is implicated in many vital cellular functions such as stem cell regeneration and organogenesis. Several intra-cellular signal transduction pathways are induced by Wnt, notably the Wnt/beta-catenin dependent pathway or canonical pathway and the non-canonical or beta-catenin-independent pathway; the latter includes the Wnt/Ca2+ and Planar Cell Polarity pathway (PCP). Wnt activation occurs at the intestinal crypt floor, and is critical to optimal maintenance of stem cells. Colorectal cancers show evidence of Wnt signaling pathway activation and this is associated with loss of function of the tumor regulator APC. Wnt activation has been observed in breast, lung, and hematopoietic malignancies and contributes to tumor recurrence. The Wnt pathway cross talks with the Notch and Sonic Hedgehog pathways, which has implications for therapeutic interventions in cancers. There are significant challenges in targeting the Wnt pathway, including finding agents that are efficacious without damaging the system of normal somatic stem cell function in cellular repair and tissue homeostasis. Here, we comprehensively review the Wnt pathway and its interactions with the Notch and Sonic Hedgehog pathways. We present the state of the field in effectors and inhibitors of Wnt signaling, including updates on clinical trials in various cancers with inhibitors of Wnt, Notch, and Sonic Hedgehog.
Keywords: Beta-catenin; Colorectal cancers; Gamma secretase; Hedgehog; Targeted therapy; Wnt.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Kurzrock has research funding from Genentech, Merck Serono, Pfizer, Sequenom, Foundation Medicine, and Guardant Health, as well as consultant fees from XBiotech and Actuate Therapeutics and an ownership interest in Novena, Inc. and Curematch, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Willert K, Brown JD, Danenberg E, Duncan AW, Weissman IL, Reya T, et al. Wnt proteins are lipid-modified and can act as stem cell growth factors. Nature. 2003 May 22;423(6938):448–52. - PubMed
-
- Bilić J, Huang YL, Davidson G, Zimmermann T, Cruciat CM, Bienz M, et al. Wnt induces LRP6 signalosomes and promotes disheveled-dependent LRP6 phosphorylation. Science. 2007 Jun 15;316(5831):1619–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

