Clustered F8 missense mutations cause hemophilia A by combined alteration of splicing and protein biosynthesis and activity
- PMID: 29170251
- PMCID: PMC5792279
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2017.178327
Clustered F8 missense mutations cause hemophilia A by combined alteration of splicing and protein biosynthesis and activity
Abstract
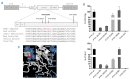
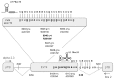
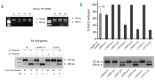
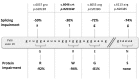
Dissection of pleiotropic effects of missense mutations, rarely investigated in inherited diseases, is fundamental to understanding genotype-phenotype relationships. Missense mutations might impair mRNA processing in addition to protein properties. As a model for hemophilia A, we investigated the highly prevalent F8 c.6046c>t/p.R2016W (exon 19) mutation. In expression studies exploiting lentiviral vectors, we demonstrated that the amino acid change impairs both Factor VIII (FVIII) secretion (antigen 11.0±0.4% of wild-type) and activity (6.0±2.9%). Investigations in patients' ectopic F8 mRNA and with minigenes showed that the corresponding nucleotide change also decreases correct splicing to 70±5%, which is predicted to lower further FVIII activity (4.2±2%), consistently with patients' levels (<1-5%). Masking the mutated exon 19 region by antisense U7snRNA supported the presence of a splicing regulatory element, potentially affected by several missense mutations causing hemophilia A. Among these, the c.6037g>a (p.G2013R) reduced exon inclusion to 41±3% and the c.6053a>g (p.E2018G) to 28±2%, similarly to a variant affecting the 5' splice site (c.6113a>g, p.N2038S, 26±2%), which displayed normal protein features upon recombinant expression. The p.G2013R reduced both antigen (7.0±0.9%) and activity (8.4±0.8%), while the p.E2018G produced a dysfunctional molecule (antigen: 69.0±18.1%; activity: 19.4±2.3%). In conclusion, differentially altered mRNA and protein patterns produce a gradient of residual activity, and clarify genotype-phenotype relationships. Data detail pathogenic mechanisms that, only in combination, account for moderate/severe disease forms, which in turn determine the mutation profile. Taken together we provide a clear example of interplay between mRNA and protein mechanisms of disease that operate in shaping many other inherited disorders.
Copyright© 2018 Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures
Comment in
-
Hemophilia A: different phenotypes may be explained by multiple and variable effects of the causative mutation in the F8 gene.Haematologica. 2018 Feb;103(2):195-196. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.186353. Haematologica. 2018. PMID: 29386375 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

