Concomitant sensitization to legumin, Fag e 2 and Fag e 5 predicts buckwheat allergy
- PMID: 29171912
- PMCID: PMC5814722
- DOI: 10.1111/cea.13068
Concomitant sensitization to legumin, Fag e 2 and Fag e 5 predicts buckwheat allergy
Abstract
Background: Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) has become increasingly popular as a healthy food in Europe. However, for sensitized individuals, consumption can cause anaphylactic reactions. The aim of this study was to identify individual well-characterized buckwheat allergens for component-resolved diagnosis.
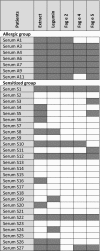
Methods: Patients were selected by positive skin prick test to buckwheat and divided into two groups: (1) sensitized to buckwheat without clinical symptoms and (2) buckwheat allergy. Buckwheat proteins were extracted from raw buckwheat seeds, purified applying a combination of protein precipitation and chromatographic methods, and analyzed by IgE immunoblotting and ELISA.
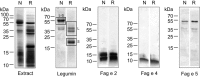
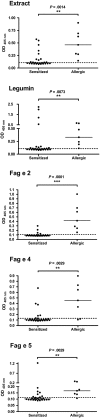
Results: Buckwheat-allergic patients had a significantly larger median skin prick test weal diameter for buckwheat than the sensitized group and the positive control. Also, IgE immunoblotting clearly showed a distinct pattern in sera from allergic patients when compared to sensitized individuals. Several IgE-reactive proteins were purified from crude buckwheat extract, namely legumin (Fag e 1 plus its large subunit), Fag e 2 (2S albumin), and newly identified Fag e 5 (vicilin-like) as well as hevein-like antimicrobial peptides, designated Fag e 4. All four allergens showed superior diagnostic precision compared to extract-based ImmunoCAP with high sensitivity as well as high specificity.
Conclusions: Patients with clinical symptoms clearly show a distinct allergen recognition pattern. We characterized a buckwheat vicilin-like protein as a new relevant marker allergen, designated Fag e 5. Additionally, another new allergen, Fag e 4, potentially important for cross-reactivity to latex was added to the allergen panel of buckwheat. Further, our data show that the full-length legumin comprising both, large and small subunit should be applied for component-resolved diagnosis. Our data indicate that concomitant sensitization to legumin, Fag e 2 and Fag e 5, predicts buckwheat allergy.
Keywords: IgE; allergens; buckwheat; component-resolved diagnosis; food allergy.
© 2017 The Authors. Clinical & Experimental Allergy Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Review on Epidemiological and Clinical Studies on Buckwheat Allergy.Plants (Basel). 2021 Mar 23;10(3):607. doi: 10.3390/plants10030607. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Usability of Fag e 2 ImmunoCAP in the diagnosis of buckwheat allergy.Arch Dermatol Res. 2011 Nov;303(9):635-42. doi: 10.1007/s00403-011-1142-z. Epub 2011 Apr 3. Arch Dermatol Res. 2011. PMID: 21461893
-
Poppy Seed Allergy: Molecular Diagnosis and Cross-Reactivity With Tree Nuts.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024 Aug;12(8):2144-2154.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2024.05.001. Epub 2024 May 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024. PMID: 38734371
-
Specific IgE for Fag e 3 Predicts Oral Buckwheat Food Challenge Test Results and Anaphylaxis: A Pilot Study.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018;176(1):8-14. doi: 10.1159/000487135. Epub 2018 Apr 10. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29635254 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical diagnosis and management of wheat and buckwheat allergy: application and prospects of allergen component diagnostics].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Nov 6;58(11):1797-1806. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20240830-00693. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39537423 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Allergens of Regional Importance in Korea.Front Allergy. 2021 Mar 5;2:652275. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2021.652275. eCollection 2021. Front Allergy. 2021. PMID: 35386990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on Epidemiological and Clinical Studies on Buckwheat Allergy.Plants (Basel). 2021 Mar 23;10(3):607. doi: 10.3390/plants10030607. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33806876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study on the reduction of Tartary buckwheat allergenicity during Pediococcus pentosaceus fermentation by HPLC-MS/MS analysis.Food Chem X. 2023 Jun 25;19:100773. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2023.100773. eCollection 2023 Oct 30. Food Chem X. 2023. PMID: 37780276 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of 2S albumin allergenic proteins for anaphylaxis in common buckwheat.Food Chem (Oxf). 2022 Jul 26;5:100127. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2022.100127. eCollection 2022 Dec 30. Food Chem (Oxf). 2022. PMID: 35968535 Free PMC article.
-
Buckwheat Allergy in Asia.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Sep;24(9):549-557. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01166-6. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 38976201 Review.
References
-
- Heffler E, Pizzimenti S, Badiu I, Guida G, Rolla G. Buckwheat allergy: an emerging clinical problem in Europe. Allergy Ther. 2014;5:2‐5.
-
- Christa K, Soral‐Smietana M. Buckwheat grains and buckwheat products ‐ Nutritional and prophylactic value of their components ‐ A review. Czech J Food Sci. 2008;26:153‐162.
-
- Takahashi Y, Ichikawa S, Aihara Y, Yokota S. Buckwheat allergy in 90,000 school children in Yokohama. Allergy. 1998;47:26‐33. - PubMed
-
- Wieslander G. Review on buckwheat allergy. Allergy. 1996;51:661‐665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

