Extended Multiple-Field High-Definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) is well tolerated and safe in healthy adults
- PMID: 29172010
- PMCID: PMC5730273
- DOI: 10.3233/RNN-170757
Extended Multiple-Field High-Definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) is well tolerated and safe in healthy adults
Abstract
Background: High definition transcranial direct current stimulation (HD-tDCS) has been administered over single brain regions for small numbers of sessions. Safety, feasibility and tolerability of HD-tDCS over multiple brain regions, multiple daily stimulations and long periods are not established.
Objective: We studied safety, feasibility and tolerability of daily HD-tDCS over 2-4 brain regions for 20 sessions in healthy adults.
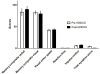
Methods: Five healthy adults underwent physical and neurological examination, electrocardiogram (EKG), electroencephalogram (EEG) and cognitive screening (ImpACT) before, during and after HD-tDCS. Four networks (left/right temporoparietal and frontal) were stimulated in sequence (20 min each) using HD-tDCS in 20 daily sessions. Sessions 1-10 included sequential stimulation of both temporoparietal networks, sessions 11-15 stimulations of 4 networks and sessions 16-20 two daily stimulation cycles of 4 networks/cycle (1.5 mA/network). Side effects, ImpACT scores and EEG power spectrum were compared before and after HD-tDCS.
Results: All subjects completed the trial. Adverse events were tingling, transient redness at the stimulation site, perception of continuing stimulation after end of session and one self-resolving headache. EEG power spectrum showed decreased delta power in frontal areas several days after HD-tDCS. While at the group level ImpACT scores did not differ before and after stimulations, we found a trend for correlation between decreased EEG delta power and individual improvements in ImpACT scores after HD-tDCS.
Conclusion: Prolonged, repeat daily stimulation of multiple brain regions using HD-tDCS is feasible and safe in healthy adults. Preliminary EEG results suggest that HD-tDCS may induce long lasting changes in excitability in the brain.
Keywords: HD-tDCS; adverse events; feasibility; safety; tolerability.
Figures



References
-
- Alonzo A, Brassil J, Taylor JL, Martin D, Loo CK. Daily transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) leads to greater increases in cortical excitability than second daily transcranial direct current stimulation. Brain Stimulation. 2012;5:208–213. - PubMed
-
- Arul-Anandam AP, Loo C, Mitchell P. Induction of hypomanic episode with transcranial direct current stimulation. Journal of ECT. 2010;26:68–69. - PubMed
-
- Baccaro A, Brunoni AR, Bensenor IM, Fregni F. Hypomanic episode in unipolar depression during transcranial direct current stimulation. Acta Neuropsychiatrica. 2010;22:316–318.
-
- Barham MP, Enticott PG, Conduit R, Lum JA. Transcranial electrical stimulation during sleep enhances declarative (but not procedural) memory consolidation: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Neuroscience and Biobehavior Reviews. 2016;63:65–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

