Dosimetric Validation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) Using AAPM TG-119 Benchmark Plans in an Upgraded CLINAC 2100CD for Flattening Filter Free (FFF) Photon Beams
- PMID: 29172266
- PMCID: PMC5773778
- DOI: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.11.2965
Dosimetric Validation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) Using AAPM TG-119 Benchmark Plans in an Upgraded CLINAC 2100CD for Flattening Filter Free (FFF) Photon Beams
Abstract
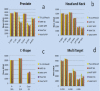
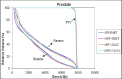
Background: Recently we have upgraded our Varian Clinac 2100CD with a 6MV FFF beam, this upgrade being the first of its kind in our country. Even though the dosimetric characteristics of FFF beams have been reported both in experimental and Monte Carlo studies, application in planning and delivery is complex. The aim of this study was to validate the commissioning of upgraded FFF beams dosimetrically using AAPM TG-119 bench mark plans for VMAT and to make a comparison with IMRT plans for both flattened filtered and FFF beams. Materials and Methods: AAPM TG-119 proposes a set of test clinical cases for testing the accuracy of IMRT planning and delivery systems. For these clinical cases we generated four treatment plans using IMRT FF, IMRT FFF, VMAT FF and VMAT FFF on a Varian Clinac 2100CD machine equipped with a millennium 120 MLC in Eclipse treatment planning system. Dose prescription and planning objectives were set according to the TG-119 goals and plans were scored based on planning objectives. Plans were compared using dose coverage, the conformity index and the homogeneity index. Point doses were measured at points recommended by TG-119 using a CC13 ion chamber. Planar dosimetry was accomplished using Imatrix and gamma evaluation was conducted using Omnipro IMRT software. Results: Dose distributions of FFF beam based plans were comparable to FF plans for both IMRT and VMAT. Our planning results matched TG-119 planning results. Measured point doses were within ±2% of planned doses and planar dosimetry gamma values were <1 for >95% of data points for all plans. Conclusion: We found a reduction of 40% treatment time for FFF against FF beams for sliding window IMRT. Upgraded FFF beams were in good agreement with TG-119 benchmark plans and goals.
Keywords: FF; FFF; VMAT; TG-119; patient specific QA.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures







References
-
- Eugenio V, Alessandro C, Giorgia N, et al. Volumetric modulated arc radiotherapy for carcinomas of the oro-pharynx, hypo-pharynx and larynx: A treatment planning comparison with fixed field IMRT. Radiother Oncol. 2009;92:111–17. - PubMed
-
- Ezzell GA, Burmeister JW, Dogan N, et al. IMRT commissioning: multiple institution planning and dosimetry comparisons, a report from AAPM Task Group 119. Med Phys. 2009;36:5359–73. - PubMed
-
- Hansen HH, Connor WG, Doppke K, Boone MML. A new field flattening filter for the clinac-4. Radiology. 1972;103:443–6. - PubMed
-
- Jatinder R, Palta Liu C, Li JG. Quality assurance of intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71:108–12. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

