Efficacy and Safety of HLD200, Delayed-Release and Extended-Release Methylphenidate, in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
- PMID: 29172680
- PMCID: PMC5567875
- DOI: 10.1089/cap.2017.0084
Efficacy and Safety of HLD200, Delayed-Release and Extended-Release Methylphenidate, in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Abstract
Objective: Evening-dosed HLD200 is a delayed-release and extended-release methylphenidate (DR/ER-MPH) formulation consisting of uniform, dual-layered microbeads with an inner drug-loaded core. DR/ER-MPH is designed to delay the initial release of drug by 8-10 hours, and thereafter, provide a controlled, extended drug release to target onset of effect upon awakening that lasts into the evening. This phase 3 study evaluated the safety and efficacy of DR/ER-MPH on symptoms and temporal at-home functional impairment in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
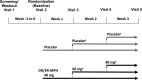
Methods: This 3-week, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, forced-dose titration trial evaluated DR/ER-MPH (40-80 mg/day) in children aged 6-12 years with ADHD. Primary efficacy endpoint was the ADHD rating scale-IV (ADHD-RS-IV), and the key secondary endpoints were the Before-School Functioning Questionnaire (BSFQ), and Parent Rating of Evening and Morning Behavior-Revised, morning (PREMB-R AM) and evening (PREMB-R PM). Safety measures included spontaneously reported treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and two TEAEs of special interest, appetite suppression and insomnia (with direct questioning on sleep disturbance).
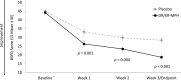
Results: One hundred sixty-one participants were included in the intent-to-treat population (DR/ER-MPH, n = 81; placebo, n = 80). After 3 weeks, DR/ER-MPH achieved significant improvements versus placebo in ADHD symptoms (least-squares [LS] mean ADHD-RS-IV: 24.1 vs. 31.2; p = 0.002), and at-home early morning (LS mean BSFQ: 18.7 vs. 28.4; p < 0.001; LS mean PREMB-R AM: 2.1 vs. 3.6; p < 0.001) and late afternoon/evening (LS mean PREMB-R PM: 9.4 vs. 12.2; p = 0.002) functional impairment. Commonly reported TEAEs (≥10%) were insomnia and decreased appetite.
Conclusions: DR/ER-MPH was generally well tolerated and demonstrated significant improvements versus placebo in ADHD symptoms and at-home functional impairments in the early morning, late afternoon, and evening in children with ADHD.
Keywords: attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; delayed-release; extended-release; functioning; methylphenidate; symptoms.
Conflict of interest statement
S.R.P. is a consultant for and has received research support from Ironshore Pharmaceuticals & Development, Inc., and has served as an expert witness for AstraZeneca. T.E.W. received grant support from NIH (NIDA); is a consultant for Alcobra, Ironshore Pharmaceuticals & Development, Inc., NIH (NIDA), Phoenix House and Bay Cove Human Services (Clinical Services), Neurovance/Otsuka, Sunovion, Tris, U.S. National Football League (ERM Associates), and U.S. Minor/Major League Baseball; has published a book,
Figures



References
-
- American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC, American Psychiatric Association, 2013
-
- Barkley RA, Cunningham CE, Gordon M, Faraone SV, Lewandowski L, Murphy KR: ADHD symptoms vs. impairments: Revisited. ADHD Rep 14:1–9, 2006
-
- Childress A, DeSousa NJ, Incledon B, McLean A, Sallee R, Lickrish D: The single dose pharmacokinetics of HLD200: A modified release methylphenidate (MPH) formulation in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Poster presented at: American Professional Society of ADHD and Related Disorders Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, 2015
-
- Childress AC: Methylphenidate HCl for the treatment of ADHD in children and adolescents. Expert Opin Pharmacother 17:1171–1178, 2016 - PubMed
-
- Childress A, Tran C: Current investigational drugs for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 25:463–474, 2016 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
