Formulation and optimization of duloxetine hydrochloride buccal films: in vitro and in vivo evaluation
- PMID: 29172829
- PMCID: PMC8241170
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2017.1402216
Formulation and optimization of duloxetine hydrochloride buccal films: in vitro and in vivo evaluation
Abstract
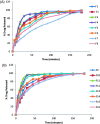
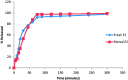
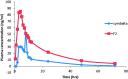
Duloxetine hydrochloride (DH) is a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SSNRI) indicated for the treatment of depression. Duloxetine suffers from reduced oral bioavailability (≈50%) due to hepatic metabolism. This study aims to develop DH buccoadhesive films to improve its bioavailability. DH buccoadhesive films were prepared adopting the solvent casting method using hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). The prepared films were evaluated for weight uniformity, drug content, surface pH, swelling index, mucoadhesion strength and drug release percentages. Accelerated stability and bioavailability studies in healthy human volunteers were also performed for the selected films. Results of the evaluation tests showed that the optimum physicochemical characters were obtained by the films prepared with 2% HPMC using 10% propylene glycol (F2 films). Accelerated stability studies revealed that DH showed proved stability throughout the experiment time. DH bioavailability from F2 films was determined and compared with that of the marketed oral capsules (Cymbalta® 30 mg). The pharmacokinetic results showed that Cmax for F2 was higher than the market product. In addition, ANOVA analysis showed that a Tmax of F2 film was significantly lower, while, the AUC0-72 of F2 was significantly higher than that of Cymbalta capsules. The percentage relative bioavailability of DH from F2 was found to be 296.39%. Therefore, the prepared buccal films offer an alternative route for the administration of DH with the possibility of improving its bioavailability.
Keywords: Buccoadhesive films; accelerated stability; bioavailability; drug release; duloxetine hydrochloride; mucoadhesion.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Abha D, Sheeja K, Bhagyashri J. (2011). Design and evaluation of buccal film of diclofenac sodium. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 1:17–30.
-
- Bendas B, Schmalfuβ U, Neubert R. (1995). Influence of propylene glycol as cosolvent on mechanisms of drug transport from hydrogels. Int J Pharm 116:19–30.
-
- Bottenberg P, Cleymaet R, De Muynck C, et al. . (1991). Development and testing of bioadhesive, fluoride-containing slow-release tablets for oral use. J Pharm Pharmacol 43:457–64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
