Cost-effectiveness of public-health policy options in the presence of pretreatment NNRTI drug resistance in sub-Saharan Africa: a modelling study
- PMID: 29174084
- PMCID: PMC5843989
- DOI: 10.1016/S2352-3018(17)30190-X
Cost-effectiveness of public-health policy options in the presence of pretreatment NNRTI drug resistance in sub-Saharan Africa: a modelling study
Abstract
Background: There is concern over increasing prevalence of non-nucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI) resistance in people initiating antiretroviral therapy (ART) in low-income and middle-income countries. We assessed the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of alternative public health responses in countries in sub-Saharan Africa where the prevalence of pretreatment drug resistance to NNRTIs is high.
Methods: The HIV Synthesis Model is an individual-based simulation model of sexual HIV transmission, progression, and the effect of ART in adults, which is based on extensive published data sources and considers specific drugs and resistance mutations. We used this model to generate multiple setting scenarios mimicking those in sub-Saharan Africa and considered the prevalence of pretreatment NNRTI drug resistance in 2017. We then compared effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of alternative policy options. We took a 20 year time horizon, used a cost effectiveness threshold of US$500 per DALY averted, and discounted DALYs and costs at 3% per year.
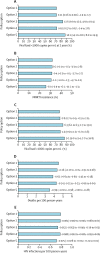
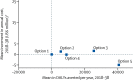
Findings: A transition to use of a dolutegravir as a first-line regimen in all new ART initiators is the option predicted to produce the most health benefits, resulting in a reduction of about 1 death per year per 100 people on ART over the next 20 years in a situation in which more than 10% of ART initiators have NNRTI resistance. The negative effect on population health of postponing the transition to dolutegravir increases substantially with higher prevalence of HIV drug resistance to NNRTI in ART initiators. Because of the reduced risk of resistance acquisition with dolutegravir-based regimens and reduced use of expensive second-line boosted protease inhibitor regimens, this policy option is also predicted to lead to a reduction of overall programme cost.
Interpretation: A future transition from first-line regimens containing efavirenz to regimens containing dolutegravir formulations in adult ART initiators is predicted to be effective and cost-effective in low-income settings in sub-Saharan Africa at any prevalence of pre-ART NNRTI resistance. The urgency of the transition will depend largely on the country-specific prevalence of NNRTI resistance.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, World Health Organization.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY IGO 3.0 licence. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Resistance to first-line ART and a role for dolutegravir.Lancet HIV. 2018 Mar;5(3):e112-e113. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(17)30207-2. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Lancet HIV. 2018. PMID: 29174085 No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2016. Consolidated guidelines on HIV prevention, diagnosis, treatment and care for key populations. 2016 update. - PubMed
-
- Justman JE, Hoos D, Kalton G, et al. Real progress in the HIV epidemic: PHIA findings from Zimbabwe, Malawi and Zambia. Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; Seattle, WA, USA; Feb 13–16, 2017. Abstract number 114LB.
-
- WHO . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2017. HIV drug resistance report 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

