Phase 1b/2a Trial of the Superoxide Dismutase Mimetic GC4419 to Reduce Chemoradiotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis in Patients With Oral Cavity or Oropharyngeal Carcinoma
- PMID: 29174131
- PMCID: PMC6430109
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.10.019
Phase 1b/2a Trial of the Superoxide Dismutase Mimetic GC4419 to Reduce Chemoradiotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis in Patients With Oral Cavity or Oropharyngeal Carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: To assess the safety of the superoxide dismutase mimetic GC4419 in combination with radiation and concurrent cisplatin for patients with oral cavity or oropharyngeal cancer (OCC) and to assess the potential of GC4419 to reduce severe oral mucositis (OM).
Patients and methods: Patients with locally advanced OCC treated with definitive or postoperative intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) plus cisplatin received GC4419 by 60-minute intravenous infusion, ending <60 minutes before IMRT, Monday through Friday for 3 to 7 weeks, in a dose and duration escalation study. Oral mucositis was assessed twice weekly during and weekly after IMRT.
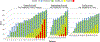
Results: A total of 46 patients received GC4419 in 11 separate dosing and duration cohorts: dose escalation occurred in 5 cohorts receiving 15 to 112 mg/d over 3 weeks (n=20), duration escalation in 3 cohorts receiving 112 mg/d over 4 to 6 weeks (n=12), and then 3 additional cohorts receiving 30 or 90 mg/d over 6 to 7 weeks (n=14). A maximum tolerated dose was not reached. One dose-limiting toxicity (grade 3 gastroenteritis and vomiting with hyponatremia) occurred in each of 2 separate cohorts at 112 mg. Nausea/vomiting and facial paresthesia during infusion seemed to be GC4419 dose-related. Severe OM occurred through 60 Gy in 4 of 14 patients (29%) dosed for 6 to 7 weeks, with median duration of only 2.5 days.
Conclusions: The safety of GC4419 concurrently with chemoradiation for OCC was acceptable. Toxicities included nausea/vomiting and paresthesia. Doses of 30 and 90 mg/d administered for 7 weeks were selected for further study. In an exploratory analysis, severe OM seemed less frequent and briefer than expected.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Sonis ST. Mucositis: The impact, biology and therapeutic opportunities of oral mucositis. Oral Oncol 45:1015–20, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Henke M, Alfonsi M, Foa P, et al.: Palifermin decreases severe oral mucositis of patients undergoing postoperative radiochemotherapy for head and neck cancer: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Clin Oncol 29:2815–20, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Le QT, Kim HE, Schneider CJ, et al.: Palifermin reduces severe mucositis in definitive chemoradiotherapy of locally advanced head and neck cancer: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Clin Oncol 29:2808–14, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Elting LS, Keefe DM, Sonis ST, et al. Patient-reported measurements of oral mucositis in head and neck cancer patients treated with radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy: Demonstration of increased frequency, severity, resistance to palliation, and impact on quality of life. Cancer 113:2704–13, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

