Efficiency and Productivity of County-level Public Hospitals Based on the Data Envelopment Analysis Model and Malmquist Index in Anhui, China
- PMID: 29176142
- PMCID: PMC5717863
- DOI: 10.4103/0366-6999.219148
Efficiency and Productivity of County-level Public Hospitals Based on the Data Envelopment Analysis Model and Malmquist Index in Anhui, China
Abstract
Background: China began to implement the national medical and health system and public hospital reforms in 2009 and 2012, respectively. Anhui Province is one of the four pilot provinces, and the medical reform measures received wide attention nationwide. The effectiveness of the above reform needs to get attention. This study aimed to master the efficiency and productivity of county-level public hospitals based on the data envelopment analysis (DEA) model and Malmquist index in Anhui, China, and then provide improvement measures for the future hospital development.
Methods: We chose 12 country-level hospitals based on geographical distribution and the economic development level in Anhui Province. Relevant data that were collected in the field and then sorted were provided by the administrative departments of the hospitals. DEA models were used to calculate the dynamic efficiency and Malmquist index factors for the 12 institutions.
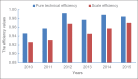
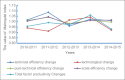
Results: During 2010-2015, the overall average relative service efficiency of 12 county-level public hospitals was 0.926, and the number of hospitals achieved an effective DEA for each year from 2010 to 2015 was 4, 6, 7, 7, 6, and 8, respectively, as measured using DEA. During this same period, the average overall production efficiency was 0.983, and the total productivity factor had declined. The overall production efficiency of five hospitals was >1, and the rest are <1 between 2010 and 2015.
Conclusions: In 2010-2015, the relative service efficiency of 12 county-level public hospitals in Anhui Province showed a decreasing trend, and the service efficiency of each hospital changed. In the past 6 years, although some hospitals have been effective, the efficiency of the county-level public hospitals in Anhui Province has not improved significantly, and the total factor productivity has not been effectively improved. County-level public hospitals need to combine their own reality to find their own deficiencies.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Zhao YW, Wu JY, Wang H, Li NN, Bian C, Xu SM, et al. Across-sectional study assessing predictors of essential medicines prescribing behavior based on information-motivation-behavioral skills model among county hospitals in Anhui, China. Chin Med J (Engl) 2015;128:2887–95. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.168046. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res. 1978;15:429–44. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(78)90138-8A.
-
- Rhodes E, Charnes A, Cooper WW. Some models for estimating technical and scale inefficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Manage Sci. 1984;30:1078–92. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.30.9.1078.
-
- Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur J Oper Res. 1978;2:429–44. doi: 10.1016/0377-2217(78)90138-8.
-
- O’Neil L, Rauner M, Hedidenberge K, Kraus M. A cross-national comparison and taxonomy of DEA-based hospital efficiency studies. Socioecon Plan Sci. 2008;42:158–89. doi: 10.1016/j.seps.2007.03.001.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous