Promising new vaccine candidates against Campylobacter in broilers
- PMID: 29176789
- PMCID: PMC5703506
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188472
Promising new vaccine candidates against Campylobacter in broilers
Abstract
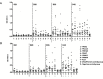
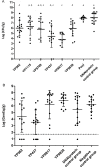
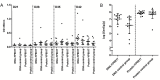
Campylobacter is the leading cause of human bacterial gastroenteritis in the European Union. Birds represent the main reservoir of the bacteria, and human campylobacteriosis mainly occurs after consuming and/or handling poultry meat. Reducing avian intestinal Campylobacter loads should impact the incidence of human diseases. At the primary production level, several measures have been identified to reach this goal, including vaccination of poultry. Despite many studies, however, no efficient vaccine is currently available. We have recently identified new vaccine candidates using the reverse vaccinology strategy. This study assessed the in vivo immune and protective potential of six newly-identified vaccine antigens. Among the candidates tested on Ross broiler chickens, four (YP_001000437.1, YP_001000562.1, YP_999817.1, and YP_999838.1) significantly reduced cecal Campylobacter loads by between 2 and 4.2 log10 CFU/g, with the concomitant development of a specific humoral immune response. In a second trial, cecal load reductions results were not statistically confirmed despite the induction of a strong immune response. These vaccine candidates need to be further investigated since they present promising features.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on Campylobacter in broiler meat production: control options and performance objectives and/or targets at different stages of the food chain. 2011.
-
- Dasti JI, Tareen AM, Lugert R, Zautner AE, Gross U. Campylobacter jejuni: a brief overview on pathogenicity-associated factors and disease-mediating mechanisms. Int J Med Microbiol. 2010;300(4):205–11. Epub 2009/08/12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2009.07.002 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wilson DJ, Gabriel E, Leatherbarrow AJ, Cheesbrough J, Gee S, Bolton E, et al. Tracing the source of campylobacteriosis. PLoS Genet. 2008;4(9):e1000203 Epub 2008/09/27. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000203 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC2538567. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- EFSA. Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Campylobacter in broiler batches and of Campylobacter and Salmonella on broiler carcasses in the EU, 2008. 2010.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

