Initial-state-dependent, robust, transient neural dynamics encode conscious visual perception
- PMID: 29176808
- PMCID: PMC5720802
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005806
Initial-state-dependent, robust, transient neural dynamics encode conscious visual perception
Abstract
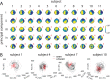
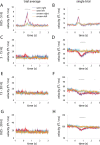
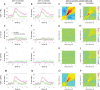
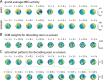
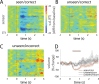
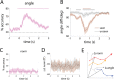
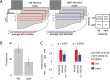
Recent research has identified late-latency, long-lasting neural activity as a robust correlate of conscious perception. Yet, the dynamical nature of this activity is poorly understood, and the mechanisms governing its presence or absence and the associated conscious perception remain elusive. We applied dynamic-pattern analysis to whole-brain slow (< 5 Hz) cortical dynamics recorded by magnetoencephalography (MEG) in human subjects performing a threshold-level visual perception task. Up to 1 second before stimulus onset, brain activity pattern across widespread cortices significantly predicted whether a threshold-level visual stimulus was later consciously perceived. This initial state of brain activity interacts nonlinearly with stimulus input to shape the evolving cortical activity trajectory, with seen and unseen trials following well separated trajectories. We observed that cortical activity trajectories during conscious perception are fast evolving and robust to small variations in the initial state. In addition, spontaneous brain activity pattern prior to stimulus onset also influences unconscious perceptual making in unseen trials. Together, these results suggest that brain dynamics underlying conscious visual perception belongs to the class of initial-state-dependent, robust, transient neural dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
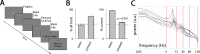

References
-
- Dehaene S. (2014) Consciousness and the Brain, Viking Press.
-
- Kahneman D. (2013) Thinking, Fast and Slow, Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
-
- Wyart V. and Tallon-Baudry C. (2009) How ongoing fluctuations in human visual cortex predict perceptual awareness: baseline shift versus decision bias. J Neurosci 29 (27), 8715–25. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0962-09.2009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ergenoglu T. et al. (2004) Alpha rhythm of the EEG modulates visual detection performance in humans. Brain Res Cogn Brain Res 20 (3), 376–83. doi: 10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2004.03.009 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mathewson K.E. et al. (2009) To see or not to see: prestimulus alpha phase predicts visual awareness. J Neurosci 29 (9), 2725–32. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3963-08.2009 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

