Inhibition of group-I metabotropic glutamate receptors protects against prion toxicity
- PMID: 29176838
- PMCID: PMC5720820
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006733
Inhibition of group-I metabotropic glutamate receptors protects against prion toxicity
Abstract
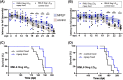
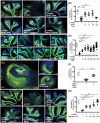
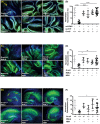
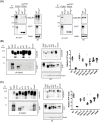
Prion infections cause inexorable, progressive neurological dysfunction and neurodegeneration. Expression of the cellular prion protein PrPC is required for toxicity, suggesting the existence of deleterious PrPC-dependent signaling cascades. Because group-I metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR1 and mGluR5) can form complexes with the cellular prion protein (PrPC), we investigated the impact of mGluR1 and mGluR5 inhibition on prion toxicity ex vivo and in vivo. We found that pharmacological inhibition of mGluR1 and mGluR5 antagonized dose-dependently the neurotoxicity triggered by prion infection and by prion-mimetic anti-PrPC antibodies in organotypic brain slices. Prion-mimetic antibodies increased mGluR5 clustering around dendritic spines, mimicking the toxicity of Aβ oligomers. Oral treatment with the mGluR5 inhibitor, MPEP, delayed the onset of motor deficits and moderately prolonged survival of prion-infected mice. Although group-I mGluR inhibition was not curative, these results suggest that it may alleviate the neurological dysfunctions induced by prion diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Fabrizio Gasparini is employed by a commercial company, Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research. Neither Dr. Gasparini nor Novartis stand to gain, directly or indirectly, from the publication of the present manuscript. All the authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Prusiner SB. Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(23):13363–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13363 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brandner S, Isenmann S, Raeber A, Fischer M, Sailer A, Kobayashi Y, et al. Normal host prion protein necessary for scrapie-induced neurotoxicity. Nature. 1996;379(6563):339–43. doi: 10.1038/379339a0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moreno JA, Halliday M, Molloy C, Radford H, Verity N, Axten JM, et al. Oral treatment targeting the unfolded protein response prevents neurodegeneration and clinical disease in prion-infected mice. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5(206):206ra138 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006767 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roucou X, Gains M, LeBlanc AC. Neuroprotective functions of prion protein. J Neurosci Res. 2004;75(2):153–61. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10864 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hernandez-Rapp J, Martin-Lanneree S, Hirsch TZ, Launay JM, Mouillet-Richard S. Hijacking PrP(c)-dependent signal transduction: when prions impair Abeta clearance. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:25 doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

