Economics of One Health: Costs and benefits of integrated West Nile virus surveillance in Emilia-Romagna
- PMID: 29176851
- PMCID: PMC5703535
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188156
Economics of One Health: Costs and benefits of integrated West Nile virus surveillance in Emilia-Romagna
Abstract
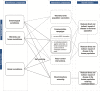
Since 2013 in Emilia-Romagna, Italy, surveillance information generated in the public health and in the animal health sectors has been shared and used to guide public health interventions to mitigate the risk of West Nile virus (WNV) transmission via blood transfusion. The objective of the current study was to identify and estimate the costs and benefits associated with this One Health surveillance approach, and to compare it to an approach that does not integrate animal health information in blood donations safety policy (uni-sectoral scenario). Costs of human, animal, and entomological surveillance, sharing of information, and triggered interventions were estimated. Benefits were quantified as the averted costs of potential human cases of WNV neuroinvasive disease associated to infected blood transfusion. In the 2009-2015 period, the One Health approach was estimated to represent a cost saving of €160,921 compared to the uni-sectoral scenario. Blood donation screening was the main cost for both scenarios. The One Health approach further allowed savings of €1.21 million in terms of avoided tests on blood units. Benefits of the One Health approach due to short-term costs of hospitalization and compensation for transfusion-associated disease potentially avoided, were estimated to range from €0 to €2.98 million according to the probability of developing WNV neuroinvasive disease after receiving an infected blood transfusion.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Macini P, Squintani G, Finarelli AC, Angelini P, Martini E, Tamba M, et al. Detection of West Nile virus infection in horses, Italy, September 2008. Euro Surveill. 2008;13(41):pii = 19002. Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=19002 - PubMed
-
- Rossini G, Cavrini F, Pierro A, Macini P, Finarelli A, Po C, et al. First human case of West Nile virus neuroinvasive infection in Italy, September 2008—case report. Euro Surveill. 2008;13(41):pii = 19002. Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=19002 - PubMed
-
- Bellini R, Calzolari M, Mattivi A, Tamba M, Angelini P, Bonilauri P, et al. The experience of West Nile virus integrated surveillance system in the Emilia-Romagna region: five years of implementation, Italy, 2009 to 2013. Euro Surveill. 2014;19(44): pii = 20953. Available online: http://www.eurosurveillance.org/ViewArticle.aspx?ArticleId=20953 - PubMed
-
- Emilia-Romagna Region. Piano di sorveglianza e controllo malattia West Nile, Chickungunya e Dengue e altri arbovirus in Emilia-Romagna, anno 2013. [Regional surveillance plan for West Nile Disease, Chickungunya, Dengue and other arboviruses in Emilia-Romagna, year 2013]. 2013. Available online: http://salute.regione.emilia-romagna.it/documentazione/piani-e-programmi...
-
- Emilia-Romagna Region. Piano sorveglianza arbovirosi 2014 [Regional arboviruses surveillance plan 2014]. 2014. Available online: http://www.izsler.it/izs_bs/allegati/736/PIANO SORVEGLIANZA ARBOVIROSI 2...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

