Interleukin-4 Receptor Alpha: From Innate to Adaptive Immunity in Murine Models of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
- PMID: 29176972
- PMCID: PMC5686050
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01354
Interleukin-4 Receptor Alpha: From Innate to Adaptive Immunity in Murine Models of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis
Abstract
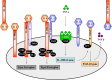
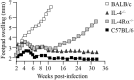
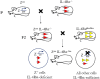
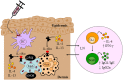
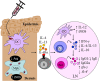
The interleukin (IL)-4 receptor alpha (IL-4Rα), ubiquitously expressed on both innate and adaptive immune cells, controls the signaling of archetypal type 2 immune regulators; IL-4 and IL-13, which elicit their signaling action by the type 1 IL-4Rα/gamma common and/or the type 2 IL-4Rα/IL-13Rα complexes. Global gene-deficient mouse models targeting IL-4, IL-13, or the IL-4Rα chain, followed by the development of conditional mice and generation of important cell-type-specific IL-4Rα-deficient mouse models, were indeed critical to gaining in-depth understanding of detrimental T helper (Th) 2 mechanisms in type 1-controlled diseases. A primary example being cutaneous leishmaniasis, which is caused by the protozoan parasite Leishmania major, among others. The disease is characterized by localized self-healing cutaneous lesions and necrosis for which, currently, not a single vaccine has made it to a stage that can be considered effective. The spectrum of human leishmaniasis belongs to the top 10 infectious diseases according to the World Health Organization. As such, 350 million humans are at risk of infection and disease, with an incidence of 1.5-2 million new cases being reported annually. A major aim of our research is to identify correlates of host protection and evasion, which may aid in vaccine design and therapeutic interventions. In this review, we focus on the immune-regulatory role of the IL-4Rα chain from innate immune responses to the development of beneficial type 1 and detrimental type 2 adaptive immune responses during cutaneous Leishmania infection. We discuss the cell-specific requirements of the IL-4Rα chain on crucial innate immune cells during L. major infection, including, IL-4Rα-responsive skin keratinocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils, as well as dendritic cells (DCs). The latter, contributing to one of the paradigm shifts with respect to the role of IL-4 instructing DCs in vivo, to promote Th1 responses against L. major. Finally, we extend these innate responses and mechanisms to control of adaptive immunity and the effect of IL-4Rα-responsiveness on T and B lymphocytes orchestrating the development of CD4+ Th1/Th2 and B effector 1/B effector 2 B cells in response to L. major infection in the murine host.
Keywords: adaptive cells; innate cells; interleukin-4 receptor alpha; interleukin-4/interleukin-13; murine cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

