The rising prevalence of obesity: part A: impact on public health
- PMID: 29177227
- PMCID: PMC5673154
- DOI: 10.1097/IJ9.0000000000000017
The rising prevalence of obesity: part A: impact on public health
Abstract
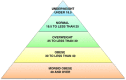
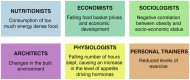
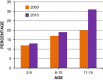
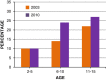
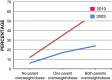
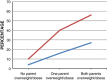
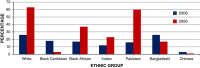
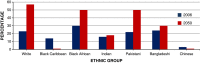
Excessive fat accumulation in the body may impair health leading to a significant long-term health consequences including the development of diabetes, coronary heart disease, and osteoarthritis as well as increasing the risk of developing certain cancers and influencing their outcomes. England has some of the worst figures and trends in obesity compared with the rest of the Europe. In the majority of European countries the trend has increased from 10% to 40% in the last 10 years, whereas in England prevalence has more than doubled. This article outlines the public health impact of rising obesity levels.
Keywords: Obesity; Overweight; Public health.
Figures
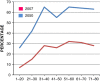
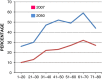
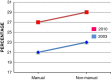
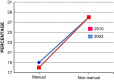

References
-
- National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. Overweight and Obesity. 2010. Available at: www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/obe/obe_whatare.html. Accessed March 4, 2012.
-
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. 2006. Available at: www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/index.html. Accessed March 28, 2012.
-
- Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Defining childhood overweight and obesity. 2011. Available at: www.cdc.gov/obesity/childhood/defining.html. Accessed March 6, 2012.
-
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). Obesity: the prevention, identification, assessment and management of overweight and obesity in adults and children. 2006. Available at: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG43. Accessed March 12, 2012.
-
- Weight Management Centre. Obesity—a public health crisis. 2010. Available at: www.wmc.uk.com/pdfs/Obesity%20Epidemic.pdf. Accessed January 14, 2012.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
