Pharmacotherapy for Neuropathic Pain: A Review
- PMID: 29178034
- PMCID: PMC5701897
- DOI: 10.1007/s40122-017-0091-4
Pharmacotherapy for Neuropathic Pain: A Review
Abstract
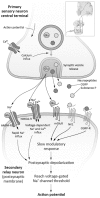
Neuropathic pain, comprising a range of heterogeneous conditions, is often severe and difficult to manage, and this may result in a chronic condition that negatively affects the overall functioning and quality of life in patients. The pharmacotherapy of neuropathic pain is challenging and for many patients effective treatment is lacking; therefore, evidence-based recommendations are essential. Currently, there is general agreement on which drugs are appropriate for the first-line treatment of neuropathic pain, whereas debate continues regarding second- and third-line treatments. First-line drugs for neuropathic pain include antidepressants (tricyclic antidepressants and serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors) and anticonvulsants acting at calcium channels (pregabalin and gabapentin). Second- and third-line drugs for neuropathic pain include topical lidocaine and opioids. Although efficacious in the treatment of neuropathic pain, opioids are not considered to be a first choice because of adverse drug reactions and, more recently, because of concerns about abuse, diversion, and addiction. A clear understanding of the mechanism of action of currently available drugs is an essential step towards an effective clinical approach that aims to tailor therapies both to the specific neuropathic disease and to the needs of an individual patient. This review provides an overview of current drugs available for the treatment of neuropathic pain with an emphasis on their mechanism of action.
Funding: Pfizer, Italy.
Keywords: Anticonvulsants; Antidepressants; Gabapentin; Mechanism of action; Neuropathic pain; Opioids; Pregabalin; Serotonin–noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors; Tricyclic antidepressants.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical