Sickle cell trait knowledge and health literacy in caregivers who receive in-person sickle cell trait education
- PMID: 29178654
- PMCID: PMC5702560
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.327
Sickle cell trait knowledge and health literacy in caregivers who receive in-person sickle cell trait education
Abstract
Background: Despite universal screening that detects sickle cell trait (SCT) in infancy, only 16% of Americans with SCT know their status. To increase SCT status awareness, effective education for patients and their families is needed. The objective of this study was to assess caregivers' SCT knowledge before and after an in-person SCT education session.
Methods: A trained educator provides in-person SCT education to caregivers of referred infants with SCT at Nationwide Children's Hospital. From August 2015 to July 2016, primarily English-speaking caregivers of infants with hemoglobin S-trait were recruited and completed a health literacy assessment and a SCT knowledge assessment (SCTKA) before and after receiving education. Caregivers repeated the SCTKA again after ≥6 months, if they could be contacted.
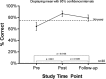
Results: Thirty-eight (38.1%) percent of 113 caregivers had high SCTKA scores (≥75%) before education but 90.3% achieved high scores after education. Caregivers with low SCTKA scores after education had significantly lower health literacy (P = 0.029) and baseline SCTKA scores (P = 0.003) compared to those with higher scores after education. At ≥6 months, caregivers' scores were significantly higher (P = 0.014) than baseline, but only 73.3% scored ≥75%.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that caregivers' baseline SCT knowledge is low, improves with in-person education but may decline with time. Caregivers who do not achieve high SCT knowledge after education had lower health literacy and baseline knowledge. Future studies should determine if adapting in-person education to caregivers' health literacy and knowledge levels results in high and sustained SCT knowledge among all caregivers and more individuals who know their SCT status.
Keywords: Health literacy and knowledge; sickle cell disease; sickle cell trait education.
© 2017 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Health Literate Approach to Address Health Disparities: a Virtual Program for Parents of Children with Sickle Cell Trait.J Commun Healthc. 2022;15(2):112-120. doi: 10.1080/17538068.2022.2026056. Epub 2022 Jan 19. J Commun Healthc. 2022. PMID: 36275941 Free PMC article.
-
Closing knowledge gaps among parents of children with sickle cell trait.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2023 Jul;70(7):e30384. doi: 10.1002/pbc.30384. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37102416
-
A pilot study to explore knowledge, attitudes, and beliefs about sickle cell trait and disease.J Natl Med Assoc. 2009 Nov;101(11):1163-72. doi: 10.1016/s0027-9684(15)31113-5. J Natl Med Assoc. 2009. PMID: 19998646
-
Reproductive attitudes and behaviors in people with sickle cell disease or sickle cell trait: a qualitative interpretive meta-synthesis.Soc Work Health Care. 2012;51(9):757-79. doi: 10.1080/00981389.2012.693580. Soc Work Health Care. 2012. PMID: 23078010 Review.
-
Sickle cell trait diagnosis: clinical and social implications.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2015;2015(1):160-7. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2015.1.160. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2015. PMID: 26637716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disease knowledge and health literacy in parents of children with sickle cell disease.EJHaem. 2023 Aug 11;4(4):956-962. doi: 10.1002/jha2.762. eCollection 2023 Nov. EJHaem. 2023. PMID: 38024626 Free PMC article.
-
A Health Literate Approach to Address Health Disparities: a Virtual Program for Parents of Children with Sickle Cell Trait.J Commun Healthc. 2022;15(2):112-120. doi: 10.1080/17538068.2022.2026056. Epub 2022 Jan 19. J Commun Healthc. 2022. PMID: 36275941 Free PMC article.
-
Sickle cell carriers' unmet information needs: Beyond knowing trait status.J Genet Couns. 2019 Aug;28(4):812-821. doi: 10.1002/jgc4.1124. Epub 2019 Apr 10. J Genet Couns. 2019. PMID: 30969464 Free PMC article.
-
A health literate evaluation of a reproductive health education program for young men with sickle cell disease.J Commun Healthc. 2025 Apr 11:1-9. doi: 10.1080/17538068.2025.2490419. Online ahead of print. J Commun Healthc. 2025. PMID: 40219642
-
Identifying Factors Underlying the Decision for Sickle Cell Carrier Screening Among African Americans Within Middle Reproductive Age.J Genet Couns. 2018 Sep;27(5):1302-1311. doi: 10.1007/s10897-018-0255-3. Epub 2018 Mar 24. J Genet Couns. 2018. PMID: 29574538
References
-
- AAP Newborn Screening Task Force . 2000. Elk Grove Village, IL. Serving the family from birth to the medical home. Newborn screening: a blueprint for the future – a call for a national agenda on state newborn screening programs. Pediatrics 106:389–422. - PubMed
-
- Asnani, M. R. , Quimby K. R., Bennett N. R., and Francis D. K.. 2016. Interventions for patients and caregivers to improve knowledge of sickle cell disease and recognition of its related complications. Cochrane Data. Syst. Rev. 10:CD011175 https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd011175.pub2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt, B. A. , Biesecker B. B., and Mastromarino C. L.. 2000. Goals, benefits, and outcomes of genetic counseling: client and genetic counselor assessment. Am. J. Med. Genet. 94:189–197. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control Data and Statistics : Children with Sickle Cell Disease. Available at https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/data.html. (Accessed 23 February 2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical