Detecting Allergens From Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon That Can Bind and Cross-link IgE by ELISA, Western Blot, and a Humanized Rat Basophilic Leukemia Reporter Cell Line RS-ATL8
- PMID: 29178679
- PMCID: PMC5705486
- DOI: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.1.62
Detecting Allergens From Black Tiger Shrimp Penaeus monodon That Can Bind and Cross-link IgE by ELISA, Western Blot, and a Humanized Rat Basophilic Leukemia Reporter Cell Line RS-ATL8
Abstract
Background: Black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon is one of the common causes of shellfish allergy that is increasing worldwide. One of the important problems in the management of shellfish allergy is the lack of accurate diagnostic assay because the biological and immunological properties of allergens in black tiger shrimp have not been well characterized. This study aims to detect proteins with the ability to bind and cross-link immunoglobulin E (IgE) from black tiger shrimp by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), Western blot, and a humanized rat basophilic leukemia reporter cell line RS-ATL8.
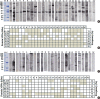
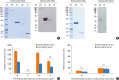
Methods: Sera from shrimp allergic subjects were subjected to ELISA and Western blots using raw or cooked shrimp extract as antigens. Pooled sera were used to sensitize the RS-ATL8 reporter cell line and cells were activated by shrimp extract. Eluted protein extracts separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) were tested on the RS-ATL8 cell line and subjected to mass spectrometry to identify potential candidate allergens.
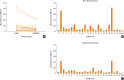
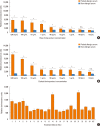
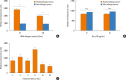
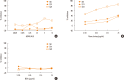
Results: Allergic sera reacted stronger to raw shrimp extract than cooked shrimp extract (P=0.009). Western blot demonstrated that major IgE reactivity protein bands were at 32-39 kDa and 91-230 kDa in both raw and cooked shrimp extracts. The eluted protein bands at the molecular weight of 38 and 115 kDa from raw shrimp extract induced IgE cross-linking as assayed by the RS-ATL8 cell line. These protein bands were subjected to mass spectrometry for analysis. Ubiquitin-activating enzyme and crustacyanin were identified as potential candidate novel shrimp allergens.
Conclusions: The RS-ATL8 reporter cell line can be used to identify potential new shrimp allergens that can functionally cross-link IgE and induce mast cell degranulation.
Keywords: IgE; Penaeus monodon; allergens; humanized basophilic leukaemia reporter cell.
Copyright © 2018 The Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology · The Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sicherer SH. Food allergy. Lancet. 2002;360:701–710. - PubMed
-
- Daul CB, Morgan JE, Hughes J, Lehrer SB. Provocation-challenge studies in shrimp-sensitive individuals. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1988;81:1180–1186. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein IL, Li JT, Bernstein DI, Hamilton R, Spector SL, Tan R, et al. Allergy diagnostic testing: an updated practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008;100:S1–S148. - PubMed
-
- Musmand JJ, Daul CB, Lehrer SB. Crustacea allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993;23:722–732. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

