MicroRNA-216a inhibits the metastasis of gastric cancer cells by targeting JAK2/STAT3-mediated EMT process
- PMID: 29179483
- PMCID: PMC5687653
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.21488
MicroRNA-216a inhibits the metastasis of gastric cancer cells by targeting JAK2/STAT3-mediated EMT process
Abstract
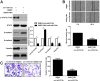
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), a group of small, non-protein coding, endogenous RNAs, play critical roles in the tumorigenesis and progression of human cancer. miR-216a has recently been reported to play an oncogenic role in human cancer. While, the expression of miR-216a, its biological function and underlying molecular mechanisms in gastric cancer (GC) are largely unknown. In this study, we revealed that miR-216a was underexpressed in GC tissues compared to matched noncancerous tissues. Decreased levels of miR-216a were confirmed in GC cell lines compared with a normal gastric epithelium cell line. miR-216a underexpression was associated with malignant prognostic features including lymph node metastasis, venous infiltration, invasive depth and advanced TNM stage. GC patients with low miR-216a level showed an obvious shorter overall survival. miR-216a overexpression restrained migration and invasion of MGC-803 cells, while its knockdown exerted opposite effects on metastatic behaviors of SGC-7901 cells. In vivo experiments found that miR-216a restoration reduced metastatic nodes of GC cells in nude mice liver. miR-216a notably suppressed epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of GC cells. Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) was recognized as a direct target and downstream mediator of miR-216a in GC cells. Interestingly, JAK2/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) pathway was prominently inactivated by miR-216a and probably mediated the role of miR-216a in the regulation of migration, invasion and EMT process of GC cells. In conclusion, these data suggest that miR-216a functions as a tumor suppressive miRNA in the development of GC possibly by targeting JAK2/STAT3-mediated EMT.
Keywords: JAK2/STAT3; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; gastric cancer; miR-216a; tumor metastasis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
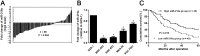






References
-
- Marques-Lespier JM, Gonzalez-Pons M, Cruz-Correa M. Current perspectives on gastric cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2016;45:413–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2016.04.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Geng R, Li J. Apatinib for the treatment of gastric cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2015;16:117–22. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.2015.981526. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhong J, Chen Y, Wang LJ. Emerging molecular basis of hematogenous metastasis in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:2434–40. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2434. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou F, Cheng L, Qiu LX, Wang MY, Li J, Sun MH, Yang YJ, Wang JC, Jin L, Wang YN, Wei QY. Associations of potentially functional variants in IL-6, JAKs and STAT3 with gastric cancer risk in an eastern Chinese population. Oncotarget. 2016;7:28112–23. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8492. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hsu KW, Fang WL, Huang KH, Huang TT, Lee HC, Hsieh RH, Chi CW, Yeh TS. Notch1 pathway-mediated microRNA-151-5p promotes gastric cancer progression. Oncotarget. 2016;7:38036–51. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9342. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

