Synaptic homeostasis requires the membrane-proximal carboxy tail of GluA2
- PMID: 29180434
- PMCID: PMC5740628
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1716022114
Synaptic homeostasis requires the membrane-proximal carboxy tail of GluA2
Abstract
Bidirectional scaling of synaptic transmission, expressed as a compensatory change in quantal size following chronic activity perturbation, is a critical effector mechanism underlying homeostatic plasticity in the brain. An emerging model posits that the GluA2 AMPA receptor (AMPAR) subunit may be important for the bidirectional scaling of excitatory transmission; however, whether this subunit plays an obligatory role in synaptic scaling, and the identity of the precise domain(s) involved, remain controversial. We set out to determine the specific AMPAR subunit required for scaling up in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons, and found that the GluA2 subunit is both necessary and sufficient. In addition, our results point to a critical role for a single amino acid within the membrane-proximal region of the GluA2 cytoplasmic tail, and suggest a distinct model for the regulation of AMPAR trafficking in synaptic homeostasis.
Keywords: AMPAR; GluA2; homeostatic plasticity; synaptic plasticity; synaptic scaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
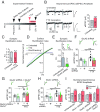

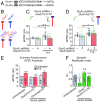
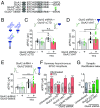

References
-
- Malinow R, Malenka RC. AMPA receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2002;25:103–126. - PubMed
-
- Collingridge GL, Isaac JT, Wang YT. Receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5:952–962. - PubMed
-
- Sheng M, Kim MJ. Postsynaptic signaling and plasticity mechanisms. Science. 2002;298:776–780. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

