mRNA Processing Factor CstF-50 and Ubiquitin Escort Factor p97 Are BRCA1/BARD1 Cofactors Involved in Chromatin Remodeling during the DNA Damage Response
- PMID: 29180510
- PMCID: PMC5789026
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00364-17
mRNA Processing Factor CstF-50 and Ubiquitin Escort Factor p97 Are BRCA1/BARD1 Cofactors Involved in Chromatin Remodeling during the DNA Damage Response
Abstract
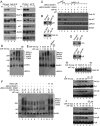
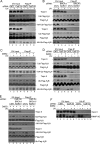
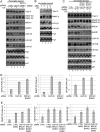
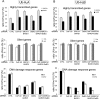
The cellular response to DNA damage is an intricate mechanism that involves the interplay among several pathways. In this study, we provide evidence of the roles of the polyadenylation factor cleavage stimulation factor 50 (CstF-50) and the ubiquitin (Ub) escort factor p97 as cofactors of BRCA1/BARD1 E3 Ub ligase, facilitating chromatin remodeling during the DNA damage response (DDR). CstF-50 and p97 formed complexes with BRCA1/BARD1, Ub, and some BRCA1/BARD1 substrates, such as RNA polymerase (RNAP) II and histones. Furthermore, CstF-50 and p97 had an additive effect on the activation of the ubiquitination of these BRCA1/BARD1 substrates during DDR. Importantly, as a result of these functional interactions, BRCA1/BARD1/CstF-50/p97 had a specific effect on the chromatin structure of genes that were differentially expressed. This study provides new insights into the roles of RNA processing, BRCA1/BARD1, the Ub pathway, and chromatin structure during DDR.
Keywords: BRCA1/BARD1; CstF-50; DNA damage response; RNA polymerase II; chromatin remodeling; histones; p97.
Copyright © 2018 Fonseca et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The BARD1 C-terminal domain structure and interactions with polyadenylation factor CstF-50.Biochemistry. 2008 Nov 4;47(44):11446-56. doi: 10.1021/bi801115g. Epub 2008 Oct 9. Biochemistry. 2008. PMID: 18842000 Free PMC article.
-
The BRCA1/BARD1 ubiquitin ligase and its substrates.Biochem J. 2021 Sep 30;478(18):3467-3483. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20200864. Biochem J. 2021. PMID: 34591954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRCA1/BARD1 inhibition of mRNA 3' processing involves targeted degradation of RNA polymerase II.Genes Dev. 2005 May 15;19(10):1227-37. doi: 10.1101/gad.1309505. Genes Dev. 2005. PMID: 15905410 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interaction of BRCA1-associated BARD1 with polyadenylation factor CstF-50.Science. 1999 Sep 3;285(5433):1576-9. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5433.1576. Science. 1999. PMID: 10477523
-
BRCA1/BARD1 is a nucleosome reader and writer.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Jul;47(7):582-595. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.03.001. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35351360 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Coordination of RNA Processing Regulation by Signal Transduction Pathways.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 7;11(10):1475. doi: 10.3390/biom11101475. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative polyadenylation: methods, mechanism, function, and role in cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Feb 1;40(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01852-7. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33526057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Tau, p53 and Pin1 Regulate PARN-Mediated Deadenylation and Gene Expression.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Oct 15;12:242. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00242. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31749682 Free PMC article.
-
DNA damage-induced transcription stress triggers the genome-wide degradation of promoter-bound Pol II.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 24;13(1):3624. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31329-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35750669 Free PMC article.
-
Connections between 3' end processing and DNA damage response: Ten years later.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020 Mar;11(2):e1571. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1571. Epub 2019 Oct 28. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2020. PMID: 31657151 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
