Efficacy of Novel Antistaphylococcal Ectolysin P128 in a Rat Model of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
- PMID: 29180523
- PMCID: PMC5786759
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01358-17
Efficacy of Novel Antistaphylococcal Ectolysin P128 in a Rat Model of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia
Abstract
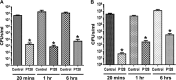
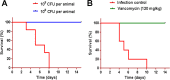
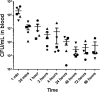
Staphylococcus aureus causes systemic infections with high morbidity and mortality, and the emergence of drug-resistant strains is a rapidly growing clinical concern. Novel therapeutic agents are required to tackle S. aureus infections. P128 is a bacteriophage-derived chimeric ectolysin with potent and rapid bactericidal activity against S. aureus In the present study, the efficacy of P128 was evaluated in a newly developed rat model of S. aureus bacteremia. Prior to in vivo testing, P128 was shown to be stable in whole blood by incubation in rat blood for up to 6 h and testing its bactericidal activity against the methicillin-resistant S. aureus isolate USA300. Rats succumbed to intravenous challenge with 109 CFU of S. aureus USA300, resulting in 80 to 100% mortality by day 14. Evaluation of the bacterial load in various organs at 96 h postinfection revealed high bacterial counts in the kidney, and this correlated with the presence of renal abscesses. Treatment of infected animals with P128 either by intravenous bolus administration via tail vein or by 1-h infusion via the jugular vein at 2 h postinfection resulted in the dose-dependent survival of rats. P128 treatment also resulted in very few or no abscesses in the kidneys. These data show that P128 is stable in the physiological milieu and that intravenous treatment with P128 is highly effective in rescuing rats from S. aureus bacteremia. P128 can be a novel therapeutic option for treatment of S. aureus systemic infections.
Keywords: P128; Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia; antibiotic resistance; ectolysin; phage lysins; renal abscesses.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures




References
-
- Daum RS. 2007. Clinical practice. Skin and soft-tissue infections caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. N Engl J Med 357:380–390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

