Examining tRNA 3'-ends in Escherichia coli: teamwork between CCA-adding enzyme, RNase T, and RNase R
- PMID: 29180590
- PMCID: PMC5824355
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.064436.117
Examining tRNA 3'-ends in Escherichia coli: teamwork between CCA-adding enzyme, RNase T, and RNase R
Abstract
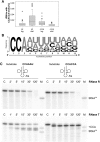
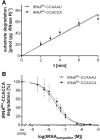
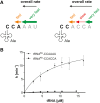
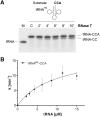
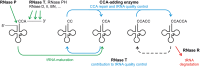
tRNA maturation and quality control are crucial for proper functioning of these transcripts in translation. In several organisms, defective tRNAs were shown to be tagged by poly(A) or CCACCA tails and subsequently degraded by 3'-exonucleases. In a deep-sequencing analysis of tRNA 3'-ends, we detected the CCACCA tag also in Escherichia coli However, this tag closely resembles several 3'-trailers of tRNA precursors targeted for maturation and not for degradation. Here, we investigate the ability of two important exonucleases, RNase R and RNase T, to distinguish tRNA precursors with a native 3'-trailer from tRNAs with a CCACCA tag. Our results show that the degrading enzyme RNase R breaks down both tRNAs primed for degradation as well as precursor transcripts, indicating that it is a rather nonspecific RNase. RNase T, a main processing exonuclease involved in trimming of 3'-trailers, is very inefficient in converting the CCACCA-tagged tRNA into a mature transcript. Hence, while both RNases compete for trailer-containing tRNA precursors, the inability of RNase T to process CCACCA tails ensures that defective tRNAs cannot reenter the functional tRNA pool, representing a safeguard to avoid detrimental effects of tRNAs with erroneous integrity on protein synthesis. Furthermore, these data indicate that the RNase T-mediated end turnover of the CCA sequence represents a means to deliver a tRNA to a repeated quality control performed by the CCA-adding enzyme. Hence, originally described as a futile side reaction, the tRNA end turnover seems to fulfill an important function in the maintenance of the tRNA pool in the cell.
Keywords: RNase R; RNase T; tRNA decay; tRNA maturation; tRNA quality control.
© 2018 Wellner et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep sequencing of tRNA's 3'-termini sheds light on CCA-tail integrity and maturation.RNA. 2020 Feb;26(2):199-208. doi: 10.1261/rna.072330.119. Epub 2019 Nov 12. RNA. 2020. PMID: 31719125 Free PMC article.
-
A tRNA's fate is decided at its 3' end: Collaborative actions of CCA-adding enzyme and RNases involved in tRNA processing and degradation.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2018 Apr;1861(4):433-441. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.01.012. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2018. PMID: 29374586 Review.
-
tRNAs marked with CCACCA are targeted for degradation.Science. 2011 Nov 11;334(6057):817-21. doi: 10.1126/science.1213671. Science. 2011. PMID: 22076379 Free PMC article.
-
How a CCA sequence protects mature tRNAs and tRNA precursors from action of the processing enzyme RNase BN/RNase Z.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 18;288(42):30636-30644. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.514570. Epub 2013 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24022488 Free PMC article.
-
The CCA-adding enzyme: A central scrutinizer in tRNA quality control.Bioessays. 2015 Sep;37(9):975-82. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500043. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Bioessays. 2015. PMID: 26172425 Review.
Cited by
-
Divergent Evolution of Eukaryotic CC- and A-Adding Enzymes.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 10;21(2):462. doi: 10.3390/ijms21020462. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31936900 Free PMC article.
-
The life and times of a tRNA.RNA. 2023 Jul;29(7):898-957. doi: 10.1261/rna.079620.123. Epub 2023 Apr 13. RNA. 2023. PMID: 37055150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carrot and stick: how RNase R contributes to function and destruction of the translation machinery.RNA Biol. 2025 Dec;22(1):1-22. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2025.2535846. Epub 2025 Jul 29. RNA Biol. 2025. PMID: 40734258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MenT nucleotidyltransferase toxins extend tRNA acceptor stems and can be inhibited by asymmetrical antitoxin binding.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 17;14(1):4644. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40264-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37591829 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymes Involved in Posttranscriptional RNA Metabolism in Gram-Negative Bacteria.Microbiol Spectr. 2018 Apr;6(2):10.1128/microbiolspec.rwr-0011-2017. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.RWR-0011-2017. Microbiol Spectr. 2018. PMID: 29676246 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Betat H, Mörl M. 2015. The CCA-adding enzyme: a central scrutinizer in tRNA quality control. Bioessays 37: 975–982. - PubMed
-
- Bradford MM. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254. - PubMed
-
- Cheng ZF, Deutscher MP. 2002. Purification and characterization of the Escherichia coli exoribonuclease RNase R. Comparison with RNase II. J Biol Chem 277: 21624–21629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
