ALKBH10B Is an RNA N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase Affecting Arabidopsis Floral Transition
- PMID: 29180595
- PMCID: PMC5757257
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.16.00912
ALKBH10B Is an RNA N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase Affecting Arabidopsis Floral Transition
Abstract
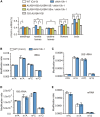
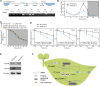
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most abundant, internal, posttranscriptional modification in mRNA among all higher eukaryotes. In mammals, this modification is reversible and plays broad roles in the regulation of mRNA metabolism and processing. Despite its importance, previous studies on the role and mechanism of m6A methylation in Arabidopsis thaliana have been limited. Here, we report that ALKBH10B is a demethylase that oxidatively reverses m6A methylation in mRNA in vitro and in vivo. Depletion of ALKBH10B in the alkbh10b mutant delays flowering and represses vegetative growth. Complementation with wild-type ALKBH10B, but not a catalytically inactive mutant (ALKBH10B H366A/E368A), rescues these effects in alkbh10b-1 mutant plants, suggesting the observed phenotypes are controlled by the catalytic action of ALKBH10B We show that ALKBH10B-mediated mRNA demethylation affects the stability of target transcripts, thereby influencing floral transition. We identified 1190 m6A hypermethylated transcripts in the alkbh10b-1 mutant involved in plant development. The discovery and characterization of the archetypical RNA demethylase in Arabidopsis sheds light on the occurrence and functional role(s) of reversible mRNA methylation in plants and defines the role of m6A RNA modification in Arabidopsis floral transition.
© 2017 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Epitranscriptomics and Flowering: mRNA Methylation/Demethylation Regulates Flowering Time.Plant Cell. 2017 Dec;29(12):2949-2950. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00929. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Plant Cell. 2017. PMID: 29203635 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abe M., Kobayashi Y., Yamamoto S., Daimon Y., Yamaguchi A., Ikeda Y., Ichinoki H., Notaguchi M., Goto K., Araki T. (2005). FD, a bZIP protein mediating signals from the floral pathway integrator FT at the shoot apex. Science 309: 1052–1056. - PubMed
-
- Alonso J.M., et al. (2003). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653–657. - PubMed
-
- Amasino R. (2010). Seasonal and developmental timing of flowering. Plant J. 61: 1001–1013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

