Linear magnetoelectric effect in göthite, α-FeOOH
- PMID: 29180762
- PMCID: PMC5703871
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-16772-w
Linear magnetoelectric effect in göthite, α-FeOOH
Abstract
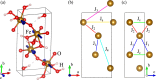
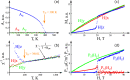
By means of symmetry analysis, density functional theory calculations, and Monte Carlo simulations we show that goethite, α-FeOOH, is a linear magnetoelectric below its Néel temperature T N = 400 K. The experimentally observed magnetic field induced spin-flop phase transition results in either change of direction of electric polarization or its suppression. Estimated value of magnetoelectric coefficient is 0.57 μC · m-2 · T-1. The abundance of goethite in nature makes it arguably the most widespread magnetoelectric material.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Scott JF. Applications of magnetoelectrics. J. Mater. Chem. 2012;22:4567–4574. doi: 10.1039/c2jm16137k. - DOI
-
- Ortega N, Kumar A, Scott JF, Katiyar RS. Multifunctional magnetoelectric materials for device applications. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter. 2015;27:504002. - PubMed
-
- Dong S, Liu J-M, Cheong S-W, Ren Z. Multiferroic materials and magnetoelectric physics: symmetry, entanglement, excitation, and topology. Adv. Phys. 2015;64:519–626. doi: 10.1080/00018732.2015.1114338. - DOI
-
- Young J, Stroppa A, Picozzi S, Rondinelli JM. Anharmonic lattice interactions in improper ferroelectrics for multiferroic design. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter. 2015;27:283202. - PubMed
-
- Cornell, R. M. & Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides: Structure, Properties, Reactions, Occurences and Uses (WILEY-VCH Verlag, Weinheim, 2003).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

