Modification and functional adaptation of the MBF1 gene family in the lichenized fungus Endocarpon pusillum under environmental stress
- PMID: 29180801
- PMCID: PMC5703946
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-16716-4
Modification and functional adaptation of the MBF1 gene family in the lichenized fungus Endocarpon pusillum under environmental stress
Abstract
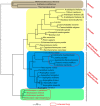
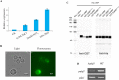
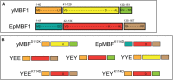
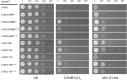
The multiprotein-bridging factor 1 (MBF1) gene family is well known in archaea, non-lichenized fungi, plants, and animals, and contains stress tolerance-related genes. Here, we identified four unique mbf1 genes in the lichenized fungi Endocarpon spp. A phylogenetic analysis based on protein sequences showed the translated MBF1 proteins of the newly isolated mbf1 genes formed a monophyletic clade different from other lichen-forming fungi and Ascomycota groups in general, which may reflect the evolution of the biological functions of MBF1s. In contrast to the lack of function reported in yeast, we determined that lysine114 in the deduced Endocarpon pusillum MBF1 protein (EpMBF1) had a specific function that was triggered by environmental stress. Further, the Endocarpon-specific C-terminus of EpMBF1 was found to participate in stress tolerance. Epmbf1 was induced by a number of abiotic stresses in E. pusillum and transgenic yeast, and its stress-resistant ability was stronger than that of the yeast mbf1. These findings highlight the evolution and function of EpMBF1 and provide new insights into the co-evolution hypothesis of MBF1 and TATA-box-binding proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The calcium-binding protein EpANN from the lichenized fungus Endocarpon pusillum enhances stress tolerance in yeast and plants.Fungal Genet Biol. 2017 Nov;108:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2017.09.003. Epub 2017 Sep 18. Fungal Genet Biol. 2017. PMID: 28927934
-
Comparative transcriptome analysis of the lichen-forming fungus Endocarpon pusillum elucidates its drought adaptation mechanisms.Sci China Life Sci. 2015 Jan;58(1):89-100. doi: 10.1007/s11427-014-4760-9. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Sci China Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25480323
-
Genome characteristics reveal the impact of lichenization on lichen-forming fungus Endocarpon pusillum Hedwig (Verrucariales, Ascomycota).BMC Genomics. 2014 Jan 17;15:34. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-34. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24438332 Free PMC article.
-
Role of multiprotein bridging factor 1 in archaea: bridging the domains?Biochem Soc Trans. 2009 Feb;37(Pt 1):52-7. doi: 10.1042/BST0370052. Biochem Soc Trans. 2009. PMID: 19143601 Review.
-
The plant MBF1 protein family: a bridge between stress and transcription.J Exp Bot. 2020 Mar 25;71(6):1782-1791. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz525. J Exp Bot. 2020. PMID: 32037452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of HbMBF1a, encoding multiprotein bridging factor 1 from the halophyte Hordeum brevisubulatum, confers salinity tolerance and ABA insensitivity to transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Mol Biol. 2020 Jan;102(1-2):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00926-7. Epub 2019 Oct 26. Plant Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31655970 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of multiprotein bridging factor 1 family genes and SlMBF1c negatively regulate the resistance to Botrytis cinerea in tomato.BMC Plant Biol. 2019 Oct 21;19(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2029-y. BMC Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31638895 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Multiprotein Bridging Factor 1-Like Protein Induces Cyst Wall Protein Gene Expression and Cyst Differentiation in Giardia lamblia.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 29;22(3):1370. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031370. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33573049 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

