Engagement of MHC class I by the inhibitory receptor LILRB1 suppresses macrophages and is a target of cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 29180808
- PMCID: PMC5832354
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-017-0004-z
Engagement of MHC class I by the inhibitory receptor LILRB1 suppresses macrophages and is a target of cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
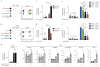
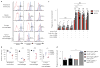
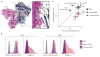
Exciting progress in the field of cancer immunotherapy has renewed the urgency of the need for basic studies of immunoregulation in both adaptive cell lineages and innate cell lineages. Here we found a central role for major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I in controlling the phagocytic function of macrophages. Our results demonstrated that expression of the common MHC class I component β2-microglobulin (β2M) by cancer cells directly protected them from phagocytosis. We further showed that this protection was mediated by the inhibitory receptor LILRB1, whose expression was upregulated on the surface of macrophages, including tumor-associated macrophages. Disruption of either MHC class I or LILRB1 potentiated phagocytosis of tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo, which defines the MHC class I-LILRB1 signaling axis as an important regulator of the effector function of innate immune cells, a potential biomarker for therapeutic response to agents directed against the signal-regulatory protein CD47 and a potential target of anti-cancer immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
K.W., A.M.R., I.L.W. and R.L.M. and are co-inventors on patent application PCT/US2015/057233, which is related to this work, and own stock of FortySeven, which is pursing clinical approval of antibody Hu5F9-G4, directed against human CD47.
Figures



Comment in
-
Another way to not get eaten.Nat Immunol. 2018 Jan;19(1):6-7. doi: 10.1038/s41590-017-0009-7. Nat Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29242546 No abstract available.
References
-
- Oldenborg PA, et al. Role of CD47 as a marker of self on red blood cells. Science. 2000;288:2051–2054. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

