The effect of CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism on adjuvant tamoxifen in Asian breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 29180876
- PMCID: PMC5692201
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S149197
The effect of CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism on adjuvant tamoxifen in Asian breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism (C 100C>T, rs1065852) on clinical outcomes of female Asian breast cancer patients with tamoxifen adjuvant treatment.
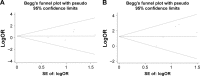
Methods: Meta-analysis of retrospective cohort studies published in July 2017 was performed. Fifteen studies with 1,794 Asian breast cancer patients were included, using strict eligibility requirements. Associations of disease-free survival (DFS), overall survival (OS) and recurrence rate after tamoxifen intake, with CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism were investigated through random effects models.
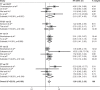
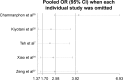
Results: CYP2D6 *10 polymorphism was found to have effect on DFS and recurrence rate in various comparison models, but not on overall survival in the female Asian breast cancer patients.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our meta-analysis suggests that significant association of *10/*10 (TT) genotype with poorer DFS and recurrence exists in female Asian breast cancer patients with tamoxifen 20 mg/day adjuvant treatment. In the future, large and well-designed studies are required to illustrate the interactions of CYP2D6 genetic variants, including *10 polymorphism and tamoxifen response on female breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Asia; CYP2D6 *10; breast cancer; polymorphism; tamoxifen adjuvant treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Fabian C, Tilzer L, Sternson L. Comparative binding affinities of tamoxifen, 4-hydroxytamoxifen, and desmethyltamoxifen for estrogen receptors isolated from human breast carcinoma: correlation with blood levels in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Biopharm Drug Dispos. 1981;2(4):381–390. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

