ALDH enzyme activity is regulated by Nodal and histamine in the A549 cell line
- PMID: 29181106
- PMCID: PMC5696712
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.7057
ALDH enzyme activity is regulated by Nodal and histamine in the A549 cell line
Abstract
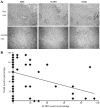
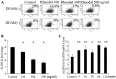
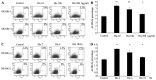
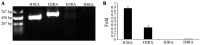
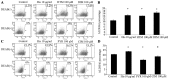
The present study aimed to examine whether the enzyme activity of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) was regulated by Nodal and histamine in the human alveolar adenocarcinoma A549 cell line. The regulated enzyme activity of ALDH was analyzed by flow cytometry in the A549 cell line. ALDH1 and Nodal expression was investigated by immunohistochemistry in28 cases of lung mixed adenocarcinoma. The enzyme activity of ALDH was upregulated by histamine and agonists of histamine H1 receptor (H1R) and histamine H2 receptor (H2R). ALDH activity was also downregulated by recombinant human Nodal and antagonists of H1R and H2R in the A549 cell line. In addition, expression of Nodal and ALDH1 were inversely correlated in lung mixed adenocarcinoma. ALDH enzyme activity was regulated by Nodal and histamine in lung adenocarcinoma.
Keywords: A549; aldehyde dehydrogenase; histamine; lung mixed adenocarcinoma; nodal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Roles of histamine on the expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 in endometrioid adenocarcinoma cell line.Cancer Med. 2014 Oct;3(5):1126-35. doi: 10.1002/cam4.296. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Cancer Med. 2014. PMID: 25045085 Free PMC article.
-
Liver alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenase: inhibition and potentiation by histamine agonists and antagonists.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1979 May-Jun;6(3):281-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1979.tb01250.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1979. PMID: 466870
-
Distinct roles of histamine H1- and H2-receptor signaling pathways in inflammation-associated colonic tumorigenesis.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Jan 1;316(1):G205-G216. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00212.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30462522 Free PMC article.
-
[Increased expression of acetaldehyde dehydrogenase in cisplatin-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma A549/DDP cells].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015 May;31(5):625-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 25940289 Chinese.
-
Effects of impromidine- and arpromidine-derived guanidines on recombinant human and guinea pig histamine H1 and H2 receptors.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2007 Jan;340(1):9-16. doi: 10.1002/ardp.200600140. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2007. PMID: 17206612
Cited by
-
Biological evaluation of levofloxacin and its thionated derivatives: antioxidant activity, aldehyde dehydrogenase enzyme inhibition, and cytotoxicity on A549 cell line.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Sep;397(9):6963-6973. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03075-x. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38613572
-
Serum deprivation-response protein regulates aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 through integrin-linked kinase signaling in endometrioid carcinoma cells.Cancer Sci. 2019 May;110(5):1804-1813. doi: 10.1111/cas.14007. Epub 2019 Apr 11. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 30907484 Free PMC article.
-
Unintended effects of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) in patients with glioblastoma (GBM): A double-edged sword.Neurooncol Pract. 2022 May 27;9(4):344-345. doi: 10.1093/nop/npac035. eCollection 2022 Aug. Neurooncol Pract. 2022. PMID: 35855453 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Egevad L, Heanue M, Berney D, Fleming K, Ferlay J. Histological groups. In: Curado MP, Edwards B, Shin HR, Storm H, Ferlay J, Heanue M, Boyle P, editors. Cancer Incidence in Five Continents. IX. IARC Scientific Publications; Lyon: 2007. pp. 62–64.
-
- Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG, Liu S, et al. ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell. 2007;1:555–567. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2007.08.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
