INTER-RATER RELIABILITY OF THE SELECTIVE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT ASSESSMENT (SFMA) BY SFMA CERTIFIED PHYSICAL THERAPISTS WITH SIMILAR CLINICAL AND RATING EXPERIENCE
- PMID: 29181253
- PMCID: PMC5685414
INTER-RATER RELIABILITY OF THE SELECTIVE FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT ASSESSMENT (SFMA) BY SFMA CERTIFIED PHYSICAL THERAPISTS WITH SIMILAR CLINICAL AND RATING EXPERIENCE
Abstract
Background: The Selective Functional Movement Assessment (SFMA) assesses posture, muscle balance, and movement patterns in order to identify relevant musculoskeletal dysfunction in a clinical population.
Purpose: The purposes of this study were to: (1) determine if raters with similar clinical experience and rating experience exhibit adequate agreement of the scoring for the SFMA during clinical use; (2) determine the reliability of the categorical scoring of the SFMA in a clinical population; (3) determine the reliability of the criterion checklist scoring of the SFMA in a clinical population; (4) compare the reliability of real-time assessment to recorded assessment.
Design: Inter-rater reliability study.
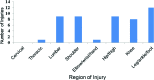
Methods: 49 clinical subjects (20.7 years ± 1.6) were simultaneously assessed in real-time by two physical therapists and were recorded with digital video cameras in the sagittal and frontal view while they performed the fifteen component movement patterns that comprise the top-tier SFMA. The third physical therapist assessed the patterns from the video. Subjects were assessed using the SFMA categorical scoring and criterion checklist scoring tools.
Results: The two live clinical raters demonstrated the greatest Cohen's Kappa scores (10 of 15) with moderate or better inter-rater agreement (Kappa > 0.40) using the categorical scoring tool. The overall ICC [2,1] score indicated fair to moderate agreement between all raters for the criterion checklist scoring (ICC, SEM, p-value) (0.61, 8.23, p < 0.001). Real time clinical use was the most reliable method for using the criterion checklist scoring tool (0.72, 1.95, p=0.43).
Conclusions: Using the categorical and criterion checklist tools in a clinical population to score the fifteen component fundamental movements of the SFMA demonstrated moderate or better reliability when performed clinically by certified SFMA raters.
Level of evidence: Reliability, Level 2.
Keywords: Dysfunction; functional movement; reliability.
Figures
References
-
- Wainner R Whitman J Cleland J Flynn T. Regional interdependence: a musculoskeletal examination model whose time has come. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2007;37(11):658-660. - PubMed
-
- Holzbaur K Murray W Delp S. A model of the upper extremity for simulating musculoskeletal surgery and analyzing neuromuscular control. Ann Biomed Eng. 2005;33(6):829-840. - PubMed
-
- Cleland JA Childs JD McRae M Palmer JA Stowell T. Immediate effects of thoracic manipulation in patients with neck pain: a randomized clinical trial. Man Ther. 2005;10(2):127-135. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials