Real-time fMRI neurofeedback of the mediodorsal and anterior thalamus enhances correlation between thalamic BOLD activity and alpha EEG rhythm
- PMID: 29181883
- PMCID: PMC6866453
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.23902
Real-time fMRI neurofeedback of the mediodorsal and anterior thalamus enhances correlation between thalamic BOLD activity and alpha EEG rhythm
Abstract
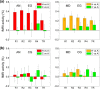
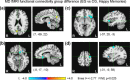
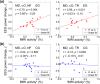
Real-time fMRI neurofeedback (rtfMRI-nf) with simultaneous EEG allows volitional modulation of BOLD activity of target brain regions and investigation of related electrophysiological activity. We applied this approach to study correlations between thalamic BOLD activity and alpha EEG rhythm. Healthy volunteers in the experimental group (EG, n = 15) learned to upregulate BOLD activity of the target region consisting of the mediodorsal (MD) and anterior (AN) thalamic nuclei using rtfMRI-nf during retrieval of happy autobiographical memories. Healthy subjects in the control group (CG, n = 14) were provided with a sham feedback. The EG participants were able to significantly increase BOLD activities of the MD and AN. Functional connectivity between the MD and the inferior precuneus was significantly enhanced during the rtfMRI-nf task. Average individual changes in the occipital alpha EEG power significantly correlated with the average MD BOLD activity levels for the EG. Temporal correlations between the occipital alpha EEG power and BOLD activities of the MD and AN were significantly enhanced, during the rtfMRI-nf task, for the EG compared to the CG. Temporal correlations with the alpha power were also significantly enhanced for the posterior nodes of the default mode network, including the precuneus/posterior cingulate, and for the dorsal striatum. Our findings suggest that the temporal correlation between the MD BOLD activity and posterior alpha EEG power is modulated by the interaction between the MD and the inferior precuneus, reflected in their functional connectivity. Our results demonstrate the potential of the rtfMRI-nf with simultaneous EEG for noninvasive neuromodulation studies of human brain function.
Keywords: EEG-fMRI; alpha rhythm; anterior nucleus; dorsal striatum; mediodorsal nucleus; memory; neurofeedback; precuneus; real-time fMRI; thalamus.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Correlation between amygdala BOLD activity and frontal EEG asymmetry during real-time fMRI neurofeedback training in patients with depression.Neuroimage Clin. 2016 Feb 12;11:224-238. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.02.003. eCollection 2016. Neuroimage Clin. 2016. PMID: 26958462 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion self-regulation training in major depressive disorder using simultaneous real-time fMRI and EEG neurofeedback.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102331. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102331. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32623140 Free PMC article.
-
Self-regulation of human brain activity using simultaneous real-time fMRI and EEG neurofeedback.Neuroimage. 2014 Jan 15;85 Pt 3:985-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.126. Epub 2013 May 11. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 23668969
-
Real-time fMRI and its application to neurofeedback.Neuroimage. 2012 Aug 15;62(2):682-92. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.009. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Neuroimage. 2012. PMID: 22019880 Review.
-
Neuromodulation of brain activation associated with addiction: A review of real-time fMRI neurofeedback studies.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102350. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102350. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32736324 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-scale neural decoding and analysis.J Neural Eng. 2021 Aug 16;18(4):10.1088/1741-2552/ac160f. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ac160f. J Neural Eng. 2021. PMID: 34284369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic functional connectivity estimation for neurofeedback emotion regulation paradigm with simultaneous EEG-fMRI analysis.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Sep 16;16:933538. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.933538. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36188168 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha Waves as a Neuromarker of Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Challenge of Reproducibility and Heterogeneity.Front Neurosci. 2018 Oct 1;12:662. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00662. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30327586 Free PMC article.
-
Frontostriatal circuitry as a target for fMRI-based neurofeedback interventions: A systematic review.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Aug 24;16:933718. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.933718. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36092647 Free PMC article.
-
REM Sleep Microstates in the Human Anterior Thalamus.J Neurosci. 2021 Jun 30;41(26):5677-5686. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1899-20.2021. Epub 2021 Apr 16. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33863786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, G. E. , Crutcher, M. D. , & DeLong, M. R. (1991). Basal ganglia‐thalamocortical circuits: Parallel substrates for motor, oculomotor, “prefrontal” and “limbic” functions. Progress in Brain Research, 85, 119–146. - PubMed
-
- Başar, E. (2012). A review of alpha activity in integrative brain function: Fundamental physiology, sensory coding, cognition and pathology. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 86, 1–24. - PubMed
-
- Bell, A. J. , & Sejnowski, T. J. (1995). An information‐maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Computation, 7, 1129–1159. - PubMed
-
- Birbaumer, N. , Ruiz, S. , & Sitaram, R. (2013). Learned regulation of brain metabolism. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 17, 295–302. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

