Elimination of tumor by CD47/PD-L1 dual-targeting fusion protein that engages innate and adaptive immune responses
- PMID: 29182441
- PMCID: PMC5825205
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2017.1409319
Elimination of tumor by CD47/PD-L1 dual-targeting fusion protein that engages innate and adaptive immune responses
Abstract
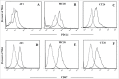
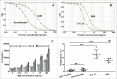
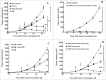
The host immune system generally serves as a barrier against tumor formation. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a critical "don't find me" signal to the adaptive immune system, whereas CD47 transmits an anti-phagocytic signal, known as the "don't eat me" signal, to the innate immune system. These and similar immune checkpoints are often overexpressed on human tumors. Thus, dual targeting both innate and adaptive immune checkpoints would likely maximize anti-tumor therapeutic effect and elicit more durable responses. Herein, based on the variable region of atezolizumab and consensus variant 1 (CV1) monomer, we constructed a dual-targeting fusion protein targeting both CD47 and PD-L1 using "Knobs-into-holes" technology, denoted as IAB. It was effective in inducing phagocytosis of tumor cells, stimulating T-cell activation and mediating antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. No obvious sign of hematological toxicity was observed in mice administered IAB at a dose of 100 mg/kg, and IAB exhibited potent antitumor activity in an immune-competent mouse model of MC38. Additionally, the anti-tumor effect of IAB was impaired by anti-CD8 antibody or clodronate liposomes, which implied that both CD8+ T cells and macrophages were required for the anti-tumor efficacy of IAB and IAB plays an essential role in the engagement of innate and adaptive immune responses. Collectively, these results demonstrate the capacity of an elicited endogenous immune response against tumors and elucidate essential characteristics of synergistic innate and adaptive immune response, and indicate dual blockade of CD47 and PD-L1 by IAB may be a synergistic therapy that activates both innate and adaptive immune response against tumors.
Keywords: CD47; PD-L1; adaptive immunity; dual-targeting fusion protein; immune checkpoint; innate immunity.
Figures


References
-
- Moynihan KD, Opel CF, Szeto GL, Tzeng A, Zhu EF, Engreitz JM, Williams RT, Rakhra K, Zhang MH, Rothschilds AM, et al.. Eradication of large established tumors in mice by combination immunotherapy that engages innate and adaptive immune responses. Nat Med. 2016;22:1402–10. doi: 10.1038/nm.4200. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
